Conflict Zones
‘Fear is real’: Why young Kashmiris are removing tattoos of guns, ‘freedom’ | India-Pakistan Tensions
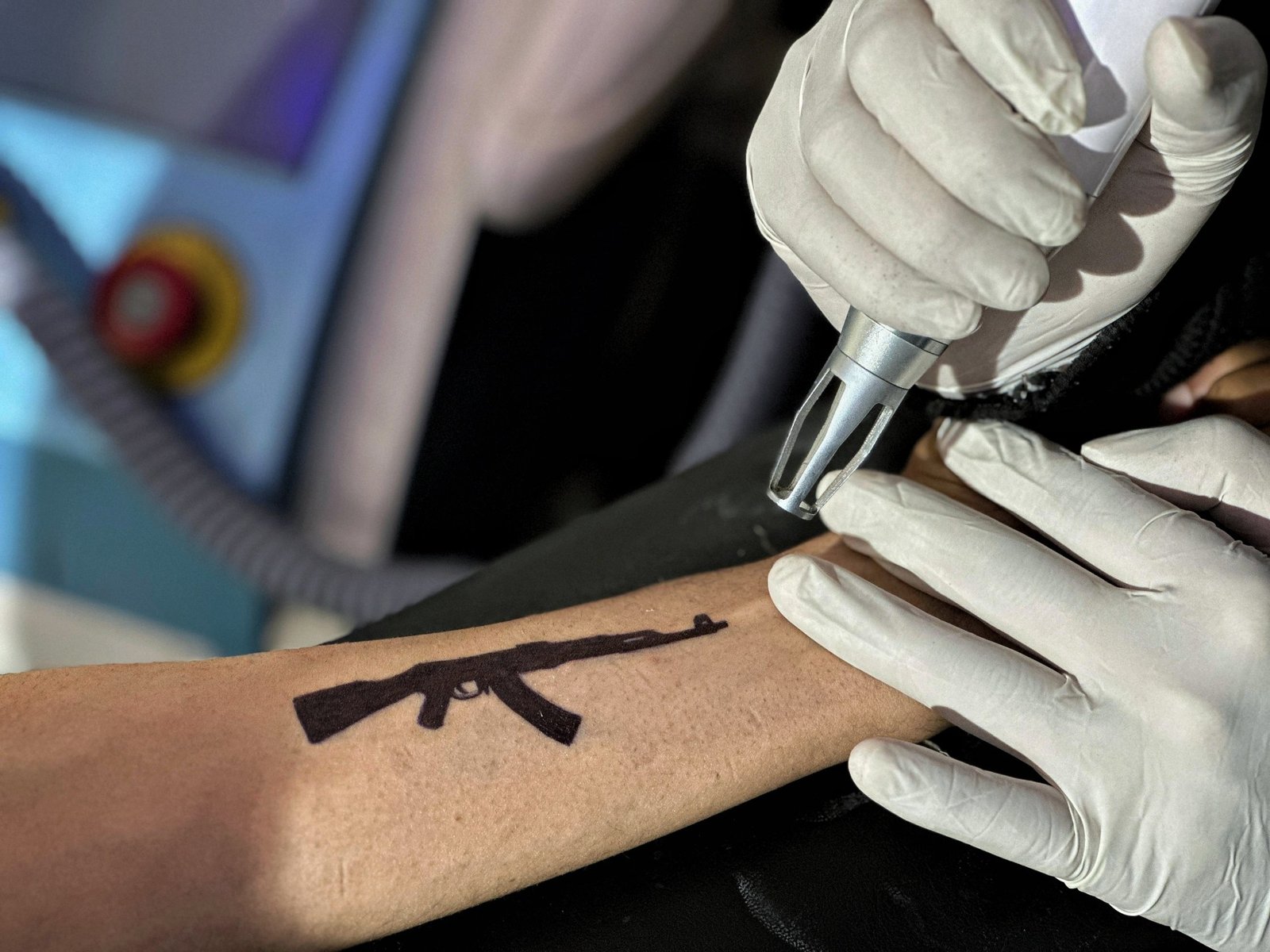
Srinagar, Indian-administered Kashmir – In a quiet laser clinic in Indian-administered Kashmir’s biggest city, Srinagar, Sameer Wani sits with his arm stretched out, his eyes following the fading ink on his skin.
The word “Azadi” (freedom in Urdu), once a bold symbol of rebellion against India’s rule, slowly disappears under the sting of the laser. What was once a mark of defiance has become a burden he no longer wants to carry.
As Sameer, 28, watches the ink vanish, his mind drifts to a day he will never forget. He was riding his motorbike with a friend when Indian security forces stopped them at a checkpoint.
During the frisking, one of the officers pointed to the tattoo on his arm and asked, “What is this?”
Sameer’s heart raced. “I was lucky he couldn’t read Urdu,” he tells Al Jazeera, his voice tinged with the memory. “It was a close call. I knew right then that this tattoo could get me into serious trouble.”
When he was younger, he said, the tattoo was a “sign of strength, of standing up for something”.
“But now I see it was a mistake. It doesn’t represent who I am any more. It’s not worth carrying the risk, and it’s not worth holding on to something that could hurt my future.”
Sameer is one of many young Kashmiris choosing to erase tattoos that once reflected their political beliefs, emotional struggles or identity. Once worn with pride, the tattoos are now being removed in growing numbers across the region – quietly and without fanfare.
While a trend to remove tattoos was already under way, the urgency has deepened since India and Pakistan – who have fought three wars over Kashmir since emerging as independent nations in 1947 – came to the brink of yet another war following the killing of 26 people in the scenic resort town of Pahalgam in Indian-administered Kashmir last month.
New Delhi accuses Islamabad of backing an armed rebellion that erupted on the Indian side in 1989. Pakistan rejects the allegation, saying it only provides moral diplomatic support to Kashmir’s separatist movement.
Two weeks after Pahalgam, India, on May 7, launched predawn drone and missile attacks on what it called “terror camps” inside Pakistan and Pakistan-administered Kashmir – the most extensive cross-border missile strikes since their war in 1971. For the next three days, the world held its breath as the South Asian nuclear powers exchanged fire until United States President Donald Trump announced a ceasefire between them on May 10.
However, peace remains fragile in Indian-administered Kashmir, where a crackdown by Indian forces has left the region gripped by fear. Homes of suspected rebels have been destroyed, others have been raided, and more than 1,500 people have been arrested since the Pahalgam attack, many under preventive detention laws.

‘We feel it on our skin’
In such a tense atmosphere, many Kashmiri youth say they feel exposed – and more vulnerable to scrutiny over even the most personal forms of expression.
“Every time something happens between India and Pakistan, we feel it on our skin – literally,” Rayees Wani, 26, a resident of Shopian district, tells Al Jazeera.
“I have a tattoo of Hurriyat leader Syed Ali Shah Geelani’s name on my arm, and after the Pahalgam attack, I started getting strange looks at checkpoints,” he said, referring to the separatist leader who passed away at the age of 91 in 2021. The Hurriyat is an alliance of pro-freedom groups in Indian-administered Kashmir.
“Even my friends ask me uncomfortable questions. The media, police, and even the neighbours start looking at you differently,” Rayees added.
“I just wish people understood that a tattoo doesn’t define someone’s loyalty or character. We are just trying to live, not explain ourselves every day. I want to erase this as soon as possible.”
Arsalan, 19, from Pulwama recently booked a tattoo removal session. He did not share his last name over fears of reprisal from the authorities.
“People with visible tattoos – especially those hinting at past political affiliations – are suddenly worried they could be profiled, questioned – or worse,” he said.
To be sure, tattoo culture itself isn’t fading in Kashmir. Tattoo studios are still busy, especially with clients aged between 22 and 40, many of whom wait for hours to get inked. But the trend has shifted; instead of political or religious tattoos, people now prefer minimalistic designs, nature-inspired patterns, names or meaningful quotes in stylish fonts.
Some Kashmiris trying to get rid of tattoos say that’s part of their personal evolution and growth.
“For me, it was about being brave,” Irfan Yaqoob from Baramulla district told Al Jazeera. Now 36, Yaqoob got a slain rebel’s name tattooed on his left arm when he was a teenager.
“Back then, it felt like a symbol of courage. But now, when I look at it, I realise how much I have changed. Life has moved on, and so have I. I have a family, a job, and different priorities. I don’t want my past to define me or create trouble in the present. That’s why I decided to get it removed. It’s not about shame. It’s about growth,” he said.

Many reasons to remove tattoos
It isn’t just the security forces that are driving this move among many Kashmiris to get rid of tattoos.
For some, tattoos became painful reminders of a turbulent past. For others, they turned into obstacles, especially when they tried to move ahead professionally or wanted to align the inscription on their bodies with their personal beliefs.
Anas Mir, who also lives in Srinagar, had a tattoo of a sword with “Azadi” written over it. He got it removed a few weeks ago.
“People don’t clearly say why they are removing tattoos. I removed mine only because of pressure from my family,” the 25-year-old said.
“It’s my choice what kind of tattoo I want. No one should judge me for it. If someone had an AK-47 or a political tattoo, that was their choice. The authorities or government shouldn’t interfere. And yes, tattoo trends also change with time,” he added, referring to the Russian-made Avtomat Kalashnikova assault rifles, arguably the most popular firearm in the world.
One of the key reasons behind people removing tattoos is religion. In a Muslim-majority region, tattoos, especially those carrying religious or political messages, could often conflict with the faith’s teachings.
Faheem, 24, had a Quranic verse tattooed on his back when he was 17.
“At that time, I thought it was an act of faith,” he told Al Jazeera, without revealing his last name over security fears. “But later, I realised that tattoos – especially with holy verses – are not encouraged [in Islam]. It started to bother me deeply. I felt guilty every time I offered namaz [prayers] or went to the mosque. That regret stayed with me. Getting it removed was my way of making peace with myself and with my faith.”
Many others said they shared the feeling. Some visit religious scholars to ask whether having tattoos affects their prayers or faith. While most are advised not to dwell on past actions, they are encouraged to take steps that bring them closer to their beliefs.
“It’s not about blaming anyone,” said Ali Mohammad, a religious scholar in Srinagar. “It’s about growth and understanding. When someone realises that something they did in the past doesn’t align with their beliefs any more, and they take steps to correct it, that’s a sign of maturity, not shame.”
Another key factor driving tattoo removals is job security. In Kashmir, government jobs are seen as stable and prestigious. But having a tattoo, especially one with political references, can create problems during recruitment or background checks.
Talib, who disclosed his first name only, had a tattoo of a Quranic verse shaped like an AK-47 rifle on his forearm. When he applied for a government position, a family friend in law enforcement hinted it might be an issue.
“He didn’t say it directly, but I could tell he was worried,” said the 25-year-old. “Since then, I have been avoiding half-sleeve shirts. I got many rejections and no one ever gave a clear reason, but deep down, I knew the tattoo was a problem. It felt like a wall between me and my future.”
As the demand for tattoo removal rises, clinics in Srinagar and other parts of Indian-administered Kashmir are seeing a steady increase in clients. Laser sessions, once rare, are now booked weeks in advance.
Mubashir Bashir, a well-known tattoo artist in Srinagar who also runs a tattoo removal service, said: “After a popular singer’s death in 2022, the trend of AK-47 tattoos exploded,” Bashir said. Punjabi singer Sidhu Moose Wala, whose music often glorified guns, was killed in May 2022. Police blamed his death on an inter-gang rivalry.
“But now, especially after the Pahalgam attack, we are seeing more people coming in to erase those tattoos. The fear is real,” Mubashir said.
He estimated that tens of thousands of tattoos have been removed in the region over the past seven years, since 2019, when India abrogated Kashmir’s semi-autonomous status and launched a major crackdown, arresting thousands of civilians. “Some say the tattoo no longer represents them. Others mention problems at work or while travelling,” Mubashir said.
Laser tattoo removal isn’t easy. It requires multiple sessions, costs thousands of rupees and can be painful. Even after successful removal, faint scars or marks often remain. But for many Kashmiris, the pain is worth it.
Sameer, whose “Azadi” tattoo is almost gone, remembers the emotional weight of the process. “I didn’t cry when I got the tattoo,” he says. “But I cried when I started removing it. It felt like I was letting go of a part of myself.”
Still, Sameer believes it was the right choice. “It’s not about shame,” he says. “I respect who I was. But I want to grow. I want to live without looking over my shoulder.”
As he finishes another laser session, a faint scar is all that is left of the word that is Kashmir’s war-cry for freedom.
“I will never forget what that tattoo meant to me when I was 18,” Sameer says as he rolls down his sleeve. “But now, I want to be someone new. I want a life where I don’t carry old shadows.”
