Africa
Red Cross closes Niger offices and foreign staff leave after junta’s expulsion order
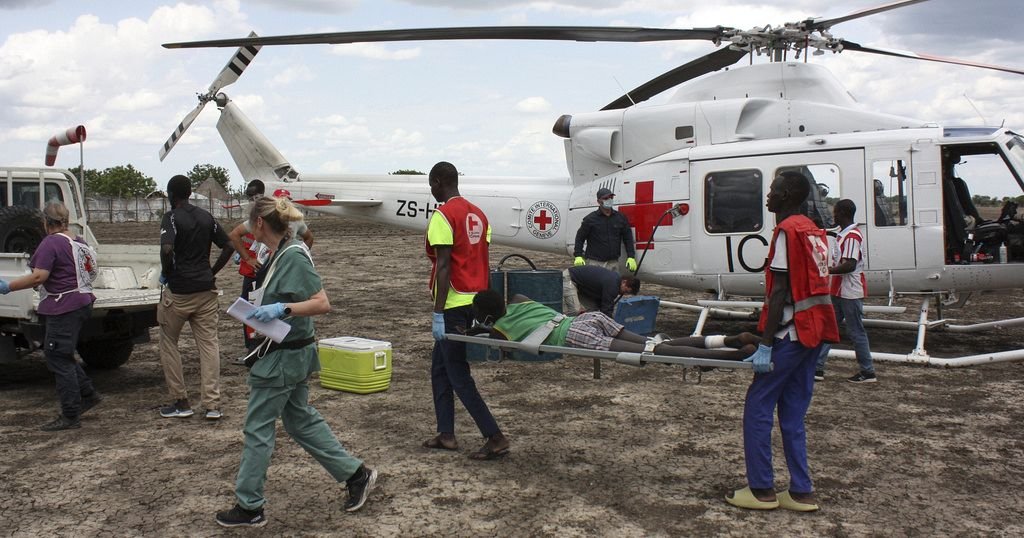
The International Committee of the Red Cross announced the closure of its offices in Niger and the departure of its foreign staff, four months after the ruling junta ordered the organization to leave the country.
The ICRC confirmed the closure and departure in a statement on Thursday.
“We reiterate our willingness to maintain constructive dialogue with the authorities of Niger with a view to resuming our strictly humanitarian protection and assistance activities,” Patrick Youssef, the ICRC’s regional director for Africa, said in the statement.
In February, Niger’s Foreign Affairs Ministry had ordered the ICRC to close its offices and leave the country. No official reason was given for the military junta’s decision to shut down the organization’s operations in the country at the time.
The ICRC said it had been in dialogue with Niger’s authorities since February to understand the reasons for their decision and provide any necessary clarification but that these efforts were unsuccessful.
On May 31, Niger’s junta leader, Abdourahamane Tchiani, justified the ICRC expulsion on Nigerien state television, accusing the organization of having met with “terrorist leaders” and funding armed groups.
The ICRC refuted the accusations in its statement on Thursday, saying that dialogue with all sides in the conflict is necessary to carry out its humanitarian mandate and that it “never provides financial, logistical, or any other form of support” to armed groups.
The humanitarian organization had been active in the West African country since 1990, mainly helping people displaced by violence by Islamic extremists, food insecurity and natural disasters. According to the organization, it provided humanitarian aid to more than 2 million people in Niger.
Niger’s military rulers took power in a coup two years ago, the latest of several military takeovers in Africa’s Sahel, the vast, arid expanse south of the Sahara Desert that has become a hotspot for extremist violence by militant groups.
Since the coup, Niger has pulled away from its Western partners, such as France and the United States, turning instead to Russia for security.
Last November, the country’s military junta banned the French aid group Acted from working in the country amid tensions with France.
Africa
Gabon launches electoral process for September 27 local and legislative elections

The electoral process for Gabon’s local and legislative elections is officially underway.
The timetable for the September 27 vote has been announced and members of the national election commission have been sworn in by the Constitutional Court.
The revision of electoral rolls across the country begins on July 14 and continues until August 12. This will ensure new voters are added and deceased or ineligible voters removed from the rolls. It will also register any changes of voting centre and update personal data.
People aged 18 and over with a Personal Identification Number (PIN) are automatically registered and need only choose their polling center.
Local electoral commissions will be set up by July 26 and deployed across the country and abroad.
Nominations for the legislative and local elections are open from July 27 to August 7.
Fifth Republic
The Ministry of the Interior and national election commission reaffirmed their commitment to ensuring “credible, transparent and peaceful” elections, and called on citizens to play an active part in building the Fifth Republic.
Last week, two years after seizing power in a coup, President Brice Oligui Nguema unveiled a new political party, the Democratic Union of Builders, or UDB. Oligui secured nearly 95 percent of the vote in April’s presidential election.
The launch of the UDB appears to signal Oligui’s intent to transition from military leader to long-term political figure. While he initially presented himself as a reformer leading a transitional government, the creation of a political party gives structure to his leadership and a platform for future governance.
Africa
Forty years and counting: CAR once again postpones local elections

Scheduled to take place for the first time in almost forty years, local and municipal elections in the Central African Republic have been once again postponed.
Initially planned for the end of August, officials say the vote will now be held in December, in conjunction with the legislative and presidential elections.
President Touadéra, who has been in office since 2016, launched a biometric voter registration exercise last year to update the electoral roll.
Authorities say the postponement is due to a delay in mobilizing funds as well as technical and organizational hiccups.
Members of the opposition BRDC are calling for an overhaul of the electoral authority and a dialogue with President Touadéra.
CAR has been battling conflict since 2013 when predominantly Muslim rebels seized power and forced the then-president from office. The United Nations has said the elections represent a ”crucial opportunity” to strengthen democratic governance, promote reconciliation and consolidate stability.
The landlocked country is one of the poorest in the world, despite having significant natural resources, including uranium, oil, gold and diamonds.
Africa
France and New Caledonia reach a deal granting territory more autonomy but no independence
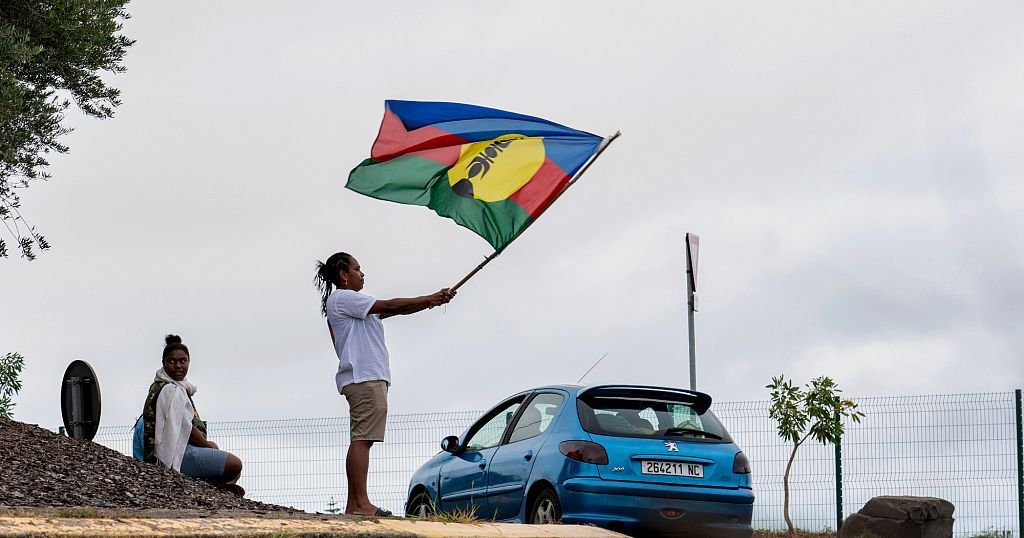

After 10 days of negotiations, including a final overnight marathon, France has reached an agreement with New Caledonia. The deal grants the South Pacific territory more autonomy — but stops short of the independence sought by many indigenous Kanaks.
President Macron hailed the deal as historic but it still needs final approval in New Caledonia. If passed, it would create a state of Caledonia within the French Republic incscribed in the French constitution and a Caledonian nationality alongside French nationality.
The talks stemmed from deadly rioting last year prompted by proposed changes to electoral rules that pro-independence groups said would marginalize Indigenous voters.
The territory has held three referenda on the question of independence, with voters each time opting to remain with France.
A special congress will be held to finalize next steps. Media reports say they could include more sovereignty for New Caledonia over international affairs, security and justice.
The accord could also eventually allow New Caledonians to change the territory’s name, flag and hymn.
Negotiators stressed the importance of rehabilitating and diversifying New Caledonia’s indebted economy, which depends heavily on nickel mining, and making it less reliant on the French mainland.
France colonized the Pacific archipelago in the 1850s, and it became an overseas territory after World War II, with French citizenship granted to all Kanaks in 1957.
-

 Asia5 days ago
Asia5 days agoA torpedoed US Navy ship escaped the Pacific in reverse, using coconut logs. Its sunken bow has just been found
-

 Asia4 days ago
Asia4 days agoGujarat state: Bridge collapse kills 9 in India
-

 Europe4 days ago
Europe4 days agoExtreme heat is a killer. A recent heat wave shows how much more deadly its becoming as humans warm the world
-

 Lifestyle5 days ago
Lifestyle5 days agoFaith-based camps like those hit by Texas floods are rite of passage for many
-

 Europe4 days ago
Europe4 days agoTrump promised 200 deals by now. He’s gotten 3, and 1 more is getting very close
-

 Africa5 days ago
Africa5 days agoCatholics in eastern Congo honor beatified anti-corruption martyr
-

 Lifestyle3 days ago
Lifestyle3 days agoHealthy workday snacks include a smart mix of energy-boosters
-

 Africa4 days ago
Africa4 days ago“Shoot in the leg”: Ruto orders Kenyan police to curb protest vandalism




