Conflict Zones
‘Inch by inch’: Myanmar rebels close in on key military base in Chin State | Military News

Falam township, Chin State – In the mountains of western Myanmar, photographs of fallen fighters line a wall of a rebel headquarters – an honour roll of some 80 young men, beginning with 28-year-old Salai Cung Naw Piang, who was killed in May 2021.
The true toll on the Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) extends beyond this hall and grows as war against Myanmar’s military grinds on in Chin State – a Christian region of the country bordering India where ethnic Chin fighters have expelled the military from most of their territory.
“Even if they don’t surrender, we will go till the end, inch by inch,” CNDF Vice President Peter Thang told Al Jazeera in a recent interview.
Launched in mid-November, the Chin offensive to capture the town of Falam – codenamed “Mission Jerusalem” – has come at a heavy cost. About 50 CNDF and allied fighters were killed in the first six weeks, some buried alive after direct air strikes by jet fighters of Myanmar’s military regime on earthen bunkers, Thang said.
Thang estimated similar casualties among Myanmar’s military, and more than 100 government soldiers captured, in the continuing operation.
Formed by civilians to fight the military after the 2021 coup in Myanmar, the CNDF has encircled the regime’s last garrison in a hilltop base in Falam.
“We are facing a difficult time,” Thang admitted.
“If God is willing to hand over the enemy, we will take it,” he said of Mission Jerusalem’s ultimate objective.
Taking and holding Falam – Chin State’s former capital – would also mark the first district centre captured by the country’s new rebel forces without support from established ethnic armies, according to Thang, who ran a travel agency in Myanmar’s commercial capital Yangon before the coup.
“We have more challenges than others,” he said.
“The military has so much technology. We have limited weapons, and even some of them we can’t operate,” he added.
![Peter Thang, Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) vice president, sits in front of the CNDF flag during an interview in a village at the frontline in Falam, Chin State, Myanmar, January 2, 2025. [Valeria Mongelli/Al Jazeera]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AB5A6226-1742020482.jpg?w=770&resize=770%2C513)
Besieged hilltop base
With the CNDF supported by fighters from 15 newly formed armed groups, including from Myanmar’s ethnic Bamar majority, about 600 rebels have besieged Falam and the roughly 120 government soldiers who, confined to their hilltop base, depend on supplies dropped by helicopter for their survival.
Unlike established ethnic armies who are fighting to gain more territory for themselves, the rebel forces massed in Chin State said they aim to overthrow Myanmar’s military regime entirely.
While the CNDF and allies in the Chin Brotherhood (CB) coalition scored previous victories against the military with help from the powerful Arakan Army (AA) to the south in Rakhine State, seizing Falam independently would represent a new phase in Myanmar’s revolution.
But the biggest challenge in the battle remains aerial attacks by the military.
Operations against the hilltop base in Falam trigger bombardments from the military’s Russian and Chinese fighter jets, along with rocket-propelled grenades, artillery, sniper and machinegun fire from troops defending the outpost.
![A Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) fighter points to the Myanmar military's base in Falam, Chin State, Myanmar, December 31, 2024. Peter Thang, Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) vice president, sits in front of the CNDF flag during an interview in a village at the frontline in Falam, Chin State, Myanmar, January 2, 2025. [Valeria Mongelli/Al Jazeera]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/0H1A3676-1742020649.jpg?w=770&resize=770%2C513)
CNDF commanders told how the besieged soldiers once chatted freely with locals and some had even married local Chin women. But that all changed when Myanmar’s security forces shot peaceful protesters demonstrating against the military’s ousting of Aung San Suu Kyi’s elected government in 2021.
Demonstrators fought back, and an uprising was born that has become steeped in blood and the lore of many martyrs.
Mya Thwe Thwe Khaing, a 19-year-old protester, was the first victim – shot in the head by police on February 9, 2021 in the country’s capital, Naypyidaw.
In April 2021, armed with hunting rifles, the Chin launched the first significant battle of Myanmar’s uprising in Mindat town, which has since been liberated.
Now the rebels are equipped with assault rifles and grenade launchers. They control most of the countryside and several towns, but remain outgunned, as the military entrenches itself in urban centres. Unable to launch ground offensives from their depleted ranks, the regime’s generals have turned to forced conscription and indiscriminate air strikes nationwide.
According to rights group the Assistance Association for Political Prisoners, the military has killed at least 6,353 civilians since the coup. With at least 3.5 million people displaced inside the country, according to the United Nations, observers predict even fiercer fighting this year.

‘Some died, others ran in all directions’
In Falam, CNDF defence secretary Olivia Thawng Luai said spouses live with some of the soldiers in the surrounded hilltop holdout.
“Most soldiers want to leave their base but they are under the commander’s control,” said Olivia Thawng Luai, a former national karate champion. “They aren’t allowed to leave the base or use their phones,” she said.
Another senior CNDF figure, Timmy Htut, said the commander in the besieged base still has his own phone – and the rebels call his number regularly.
“One day he will pick up,” he said. “When he’s ready.”
Attempts by the military to send reinforcements to Falam have failed. Helicopters, facing sheets of gunfire, have dropped conscripted airborne recruits on Falam’s outskirts, ordering them to fight their way into the town. None has succeeded.
![Olivia Thawng Luai, Chin National Defence Force (CNDF)'s defence secretary, is portrayed in a village at the frontline in Falam, Chin State, Myanmar, January 1, 2025. [Olivia Thawng Luai, Chin National Defence Force (CNDF)'s defence secretary, sits in front of the CNDF flag during an interview in a village at the frontline in Falam, Chin State, Myanmar, January 1, 2025 A Chin National Defence Force (CNDF) fighter stands on the ruins of a church bombed by a Myanmar military jet in Falam township, Chin State, Myanmar, December 31, 2024. [Valeria Mongelli/Al Jazeera]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/AB5A6023-1742020999.jpg?w=770&resize=770%2C513)
A captured soldier said his unit was dropped in without a plan, and, under heavy fire and pursued by resistance fighters, they scattered in chaos.
“Some died, others ran in all directions,” the soldier told Al Jazeera.
“The headquarters said they couldn’t waste their jet sorties for just a few of us,” he said. The military, he continued, has lost “many skilful, valuable” soldiers since the coup.
“They gave their lives for nothing,” he said.
“In the end, the military leaders will offer peace talks, and there will probably be democracy.”
Among the people displaced by fighting in Falam, and who are forced to shelter under bridges and tarpaulins, a new generation prepares to fight.
Junior, 15, who assists at a Chin hospital camp, spoke from an air raid shelter within earshot of jets dropping bombs.
“I’ll do whatever I can,” Junior said. “There’s no way to study in Myanmar. I don’t want future generations to face this,” she said.

‘None of you would be alive’
But the Chin resistance is also grappling with internal division. It has split into two factions: one led by the Chin National Front (CNF), established in 1988, along with its allies, and the other, the Chin Brotherhood, comprising six post-coup resistance groups, including the CNDF.
Their dispute centres on who shapes Chin’s future – the CNF favouring a dialect-based governance structure, the CB preferring the governing of townships. This distinction between language and land determines the distribution of power, and, coupled with tribal rivalries and traditional mistrust, has led to occasional violent clashes among the Chin groups.
Myanmar analyst R Lakher described the divide as “serious”, though mediation efforts by northeast India’s Mizoram authorities show progress.
On February 26, the two rival factions announced they would merge to form the Chin National Council, with a goal of uniting different armed groups under one military leadership and administration.
While welcoming the development, Lakher stressed the process must be “very systematic” and include key political leaders from either side, not only advocacy groups.
“Chin civilians have suffered most,” he said. “Despite liberation, some cannot return home because of this internal conflict.”
Capturing Falam would be “significant”, he said, as nearby Tedim town would then present an easier target, potentially freeing up more territory for the CB and strengthening their negotiating position with the CNF coalition.
Lakher estimated more than 70 percent of Chin State has been liberated.
“We’ve seen the junta being defeated across Myanmar,” he said. “But pro-democracy forces need unity.”
He said the onus was on the National Unity Government – described as Myanmar’s shadow government – to “bring all democratic forces together”.
“With so many armed groups, there’s concern they’ll fight each other without strong leadership,” he said. “Ethnic areas are being liberated while Bamar lands remain under military control. The revolution’s pace now depends on the Bamar people.”

Along the road leading out of Falam town, two trucks loaded with captured regime soldiers drove past Chin’s bombed churches, gardens of mustard leaf, and mothers cradling babies under heavy shawls. As the trucks crossed paths with resistance fighters heading to the front, the nervous prisoners of war claimed they had been forced into military service.
“You were conscripted five months ago,” a rebel fighter remonstrated with prisoners in the truck. “What were you doing before then? he asked. He then added: “We’ve been fighting the revolution.”
Another rebel joined in the rebuke.
“Count yourselves lucky to be captured here,” he said – and not in the country’s harsh central drylands, where rebel units roam unchecked.
“None of you would be alive there,” he added.
Conflict Zones
Ballet helps fight war fatigue in Ukraine’s front-line Kharkiv city | Russia-Ukraine war

In the Ukrainian city of Kharkiv, escaping the war with Russia is nearly impossible.
On certain days, when the wind shifts, residents of this historic city can hear the distant rumble of artillery fire from the front line, some 30km (18.5 miles) away.
Most nights, Russian kamikaze drones packed with explosives buzz overhead as parents put their children to bed.
Three years since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the unrelenting war exerts a heavy psychological burden on many in Kharkiv. Yet, there is a place in the city where, for a few fleeting hours, the war seems to vanish.
Beneath the Kharkiv National Academic Opera and Ballet Theatre, in a dim, brick-walled basement, a dance company has established a refuge from drones and bombs – a space where audiences can lose themselves in performances of classic ballets.
In April, this underground venue hosted performances of Chopiniana, an early 20th-century ballet set to the music of Frederic Chopin. Despite the improvised setting, the ballet was staged with full classical grandeur, complete with corps de ballet and orchestra.

It marked a significant milestone for Kharkiv’s cultural life: the first complete classical ballet performance in the city since February 2022, when Russian troops launched their invasion of Ukraine.
“In spite of everything – the fact that bombs are flying, drones, and everything else – we can give a gift of something wonderful to people,” said Antonina Radiievska, artistic director of Opera East, the ballet company behind the production.
“They can come and, even if it’s just for an hour or two, completely immerse themselves in a different world.”
Despite Ukraine’s rich tradition in classical ballet, the art form now seems far removed from the everyday existence of Ukrainians living through war. Daily routines revolve around monitoring apps for drone alerts, sleeping on metro station floors to escape air raids, or seeking news of loved ones on the front line. Pirouettes, pas de deux and chiffon tutus feel worlds away.
Nevertheless, the journey of Kharkiv’s ballet through wartime reflects the ways in which Ukrainian society has adapted and evolved.
On February 23, 2022, the National Academic Opera and Ballet Theatre staged a performance of the ballet Giselle. The next day, Russia launched its full-scale invasion. As Moscow’s forces advanced towards Kharkiv and threatened to seize the city, the theatre closed its doors and much of the ballet troupe departed.
Some regrouped in Slovakia and Lithuania, mounting ballet productions abroad with assistance from European sponsors.

By 2023, although the conflict ground on, the situation in Kharkiv, in Ukraine’s northeast, had stabilised after Russian ground troops withdrew. A new realisation took hold – this was a long-term reality. Locals began referring to the city, and themselves, with the Ukrainian word “nezlamniy”, meaning invincible.
That year, work began on transforming the theatre’s basement into a performance venue. By October 2023, it was being used for rehearsals. The following spring, authorities permitted the theatre to admit audiences, and small-scale ballet performances, including children’s concerts, resumed.
The revival of Chopiniana marked the next chapter in Kharkiv’s wartime cultural journey.
Staging a classical opera again signals that Ukraine endures, says Igor Tuluzov, director-general of Opera East. “We are demonstrating to the world that we really are a self-sufficient state, independent, in all its aspects, including cultural independence,” he said.
The auditorium now seats 400 people on stackable chairs, compared with the 1,750 seats in the main theatre above, where the plush mustard seats remain empty.
The stage is a quarter the size of the main one. Grey-painted bricks, concrete floors, and exposed pipes and wiring form a stark contrast to the varnished hardwood and marble of the theatre above. The basement’s acoustics, performers say, fall short of the cavernous main auditorium.
For artistic director Radiievska, however, the most important thing is that, after a long pause, she and her troupe can once again perform for a live audience.
“It means, you know, life,” she said. “An artist cannot exist without the stage, without creativity, without dance or song. It’s like a rebirth.”
Conflict Zones
Sudan Paramilitary Claims Key Gains in Kordofan; Fighting Intensifies Near Khartoum
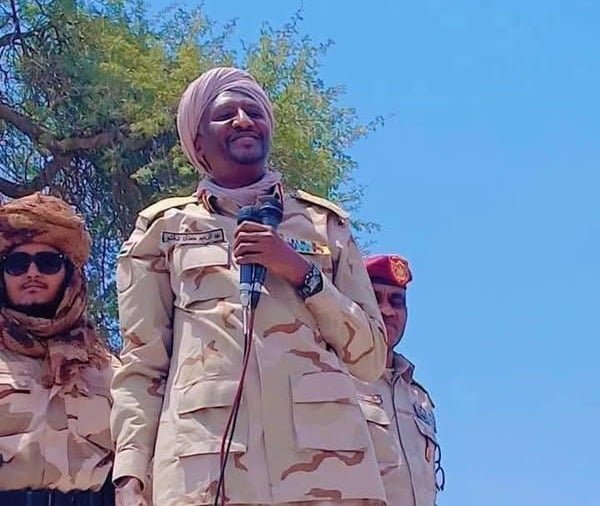

Khartoum, May 30, 2025 — Rapid Support Forces (RSF) deputy leader Abdel Rahim Daglo announced on Friday that RSF fighters would press their eastward advance toward Khartoum, claiming “great victories” in several strategic towns across Kordofan. Addressing troops at an undisclosed location, Daglo said that all armed groups within the Tasis coalition had joined his paramilitary ranks and were now operating in concert with the RSF.
According to Daglo, RSF units seized control of Al-Dubaibat and Al-Hammadi in South Kordofan state, as well as Al-Khawi in neighboring West Kordofan. “Our fighters have secured these areas after intense clashes with Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) units and allied militias,” Daglo declared, adding that the momentum would not wane until the capital was within reach.
Sudan’s army, however, downplayed recent RSF advances as part of a “reorganization” campaign. A senior ally of the SAF—also the governor of Darfur—insisted that the military was regrouping and fortified its positions to counter what he described as “a temporary setback.” He maintained that the SAF’s strategic reserves remained intact and that front-line forces were being repositioned to mount a sustained defense of Khartoum.
As fighting has spread northward, the humanitarian situation in Khartoum has deteriorated sharply. With basic services all but collapsed, a deadly cholera outbreak has emerged in the densely populated capital. Aid agencies warn that the impending rainy season could exacerbate sanitation challenges, fueling further disease transmission. The United Nations has labeled the crisis “the world’s worst humanitarian emergency,” citing over 25,000 confirmed deaths and more than 3 million internally displaced persons since April.
International pressure has also mounted on Sudan’s transitional government. In late May, Washington imposed sanctions on Sudanese military leaders for the “alleged use of chemical weapons” against civilians. In response, the government announced a national investigation into the claims—a move it said was aimed at preserving Sudan’s international standing amid intensifying conflict.
With both sides entrenching their positions around Khartoum, observers warn that a protracted stalemate could unleash further civilian suffering. The RSF’s pledge to advance eastward has raised concerns that front-line engagements may spill into densely populated suburbs, where millions have already endured weeks of intermittent shelling and aerial bombardments. For now, the fate of Khartoum—and the broader prospects for peace—remain uncertain as paramilitary and army forces brace for a decisive showdown.
Conflict Zones
Two killed in Russian attacks on Ukraine before possible talks in Turkiye | Russia-Ukraine war News
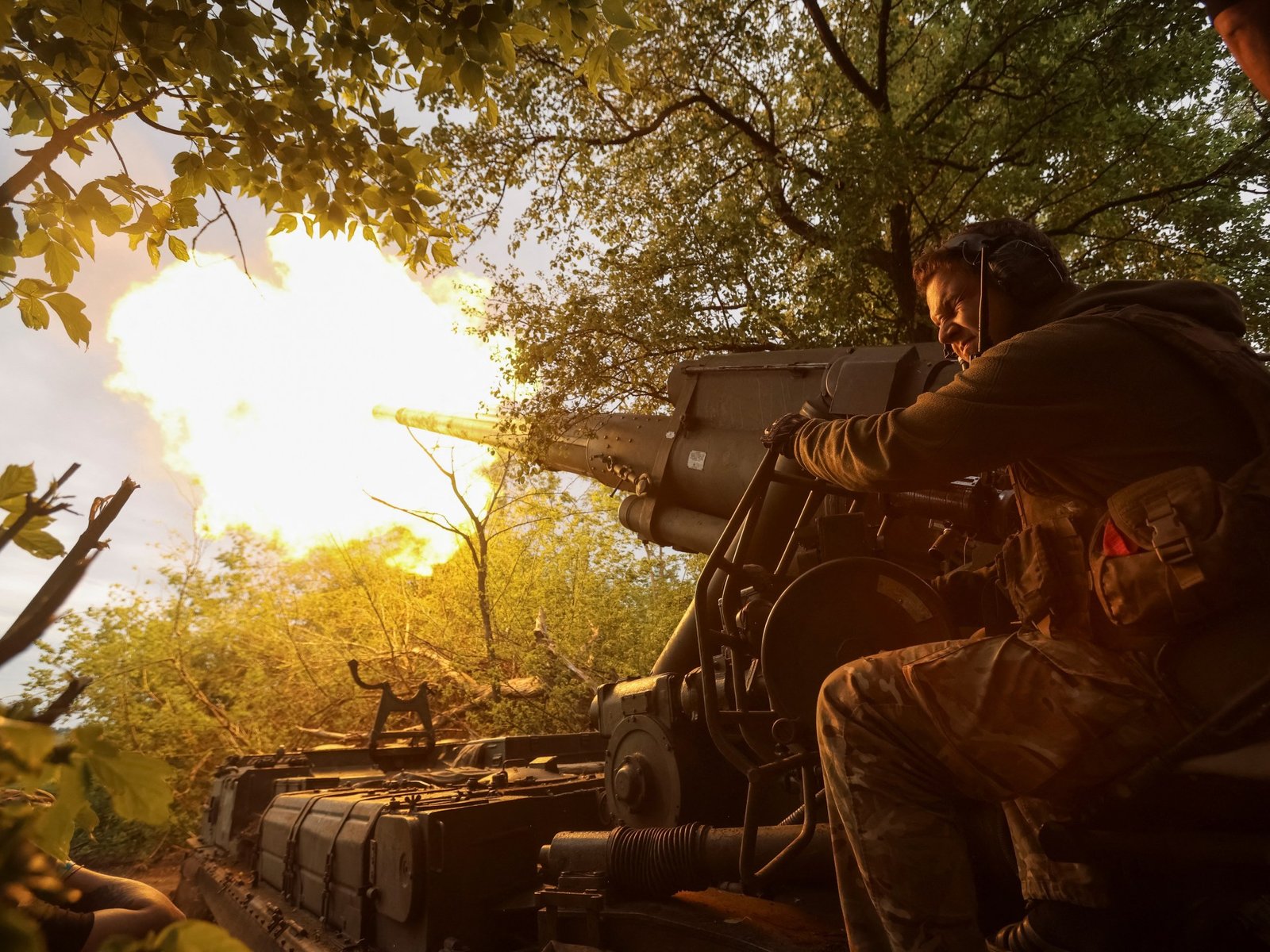

Russia has confirmed it will send a delegation to Istanbul, but Kyiv has not yet accepted the proposal.
Russian drone and missile attacks on Ukraine have killed at least two people, according to officials, as Ukraine ordered the evacuation of 11 more villages in its Sumy region bordering Russia.
Russian troops launched an estimated 109 drones and five missiles across Ukraine on Friday and overnight, the Ukrainian air force said on Saturday, adding that three of the missiles and 42 drones were destroyed and another 30 drones failed to reach their targets without causing damage.
The attacks came amid uncertainty over whether Kyiv will take part in a new round of peace talks early next week in Istanbul.
In the Russian attacks on Saturday, a child was killed in a strike on the front-line village of Dolynka in the Zaporizhia region, and another was injured, Zaporizhia’s Governor Ivan Fedorov said.
“One house was destroyed. The shockwave from the blast also damaged several other houses, cars, and outbuildings,” Fedorov wrote on Telegram.
A man was also killed by Russian shelling in Ukraine’s Kherson region, Governor Oleksandr Prokudin wrote on Telegram.
Moscow did not comment on either attack.
Meanwhile, authorities in Ukraine’s Sumy region said they were evacuating 11 villages within a roughly 30-kilometre (19-mile) range from the Russian border.
“The decision was made in view of the constant threat to civilian life as a result of shelling of border communities,” the regional administration said on social media.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has said some 50,000 Russian troops have amassed in the area with the intention of launching an offensive to carve out a buffer zone inside Ukrainian territory.
Ukraine’s top army chief, Oleksandr Syrskii, said on Saturday that Russian forces were focusing their main offensive efforts on Pokrovsk, Torets and Lyman in the Donetsk region, as well as the Sumy border area.
Syrskii added that Ukrainian forces are still holding territory in Russia’s Kursk region – a statement Moscow has repeatedly denied.
The evacuations and attacks came just two days before a possible meeting between Kyiv and Moscow in Istanbul, as Washington called on both countries to end the three-year war.
Russia has confirmed it will send a delegation, but Kyiv has not yet accepted the proposal, warning the talks would not yield results unless the Kremlin provided its peace terms in advance.
Zelenskyy said Saturday it was still not clear what Moscow was planning to achieve at the meeting and that so far, it did not “look very serious”.
-

 Africa4 days ago
Africa4 days agoSurvivor of Liverpool car ramming talks of shock and panic
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoThe Knicks are bringing hope and title dreams back to New York after years in the doldrums
-

 Lifestyle4 days ago
Lifestyle4 days agoFaizan Zaki hopes to go from spelling bee runner-up to champ
-

 Lifestyle3 days ago
Lifestyle3 days agoChildren and careers: Talking to kids about what they want to be when they grow up
-

 Lifestyle4 days ago
Lifestyle4 days agoHow to decorate a patio, balcony or other small outdoor space
-

 Europe5 days ago
Europe5 days agoMacron’s marital shove disappears from French airwaves
-
 Middle East4 days ago
Middle East4 days agoThe cost of conscience: I lost friends for defending Palestinians | Israel-Palestine conflict
-

 Middle East5 days ago
Middle East5 days agoHajj pilgrimage in Saudi Arabia to begin on June 4 | Religion News




