Lifestyle
Kennedy and influencers bash seed oils, baffling nutrition scientists
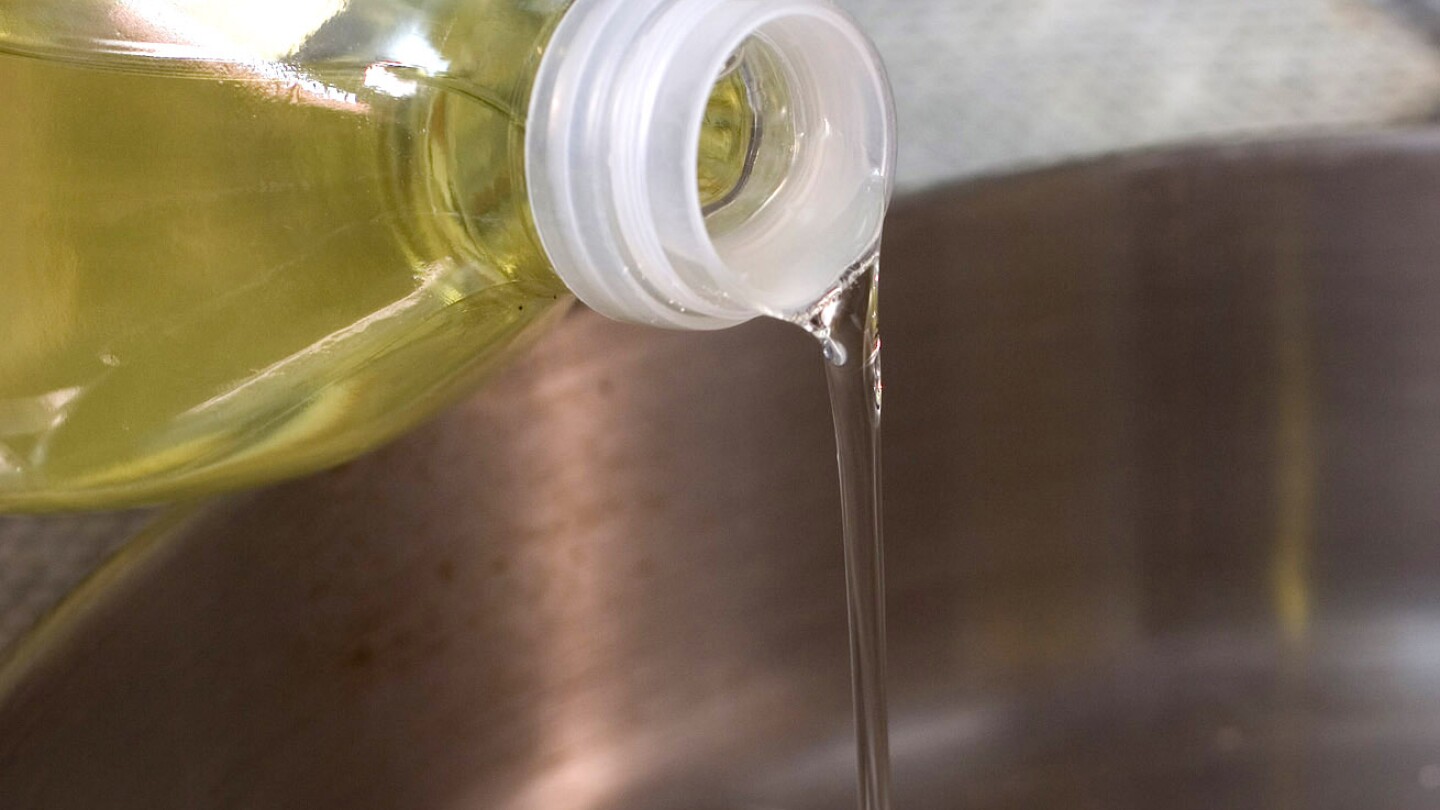

Until recently, most Americans had never heard the term “seed oils,” even though they’ve likely cooked with and consumed them for decades.
It’s the catchy description coined by internet influencers, wellness gurus and some politicians to refer to common cooking oils — think canola, soybean and corn oil — that have long been staples in many home kitchens.
Those fiery critics refer to the top refined vegetable oils as “the hateful eight” and claim that they’re fueling inflammation and high rates of chronic diseases like obesity and diabetes.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr., the new health secretary, has said Americans are being “unknowingly poisoned” by seed oils and has called for fast-food restaurants to return to using beef tallow, or rendered animal fat, in their fryers instead.
In response to consumer concerns, some food-makers have stripped seed oils from their products. Restaurants like the salad chain Sweetgreen have removed them from their menus. Many Americans say they now avoid seed oils, according to a recent survey from the International Food Information Council, an industry trade group.
The seed oil discussion has exasperated nutrition scientists, who say decades of research confirms the health benefits of consuming such oils, especially in place of alternatives such as butter or lard.
“I don’t know where it came from that seed oils are bad,” said Martha Belury, an Ohio State University food science professor.
In a Senate hearing Thursday, Dr. Marty Makary, nominated to lead the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, called for a closer review of the products.
“I think seed oils are a good example of where we could benefit from a consolidation of the scientific evidence,” he said.
What are seed oils?
Simply put, they are oils extracted from plant seeds. They include eight commonly targeted by critics: canola, corn, cottonseed, grapeseed, soybean, sunflower, safflower and rice bran.
Seed oils are typically made by pressing or crushing the seeds and then processing them further with chemicals and heat to remove elements that can leave the oil cloudy or with an unpleasant taste or odor.
The result of such refining is a neutral-tasting oil that is inexpensive, shelf-stable and able to be heated at a high temperature without smoking, said Eric Decker, a food science professor at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
By contrast, olive oil and avocado oil are considered fruit oils. They’re often cold-pressed, which retains many of the plant-based compounds that benefit health — but also makes the oils more expensive and prone to smoking at high heat.
Seed oils are composed mostly of unsaturated fatty acids, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat. Most seed oils are high in one type of fatty acid, omega-6, and low in another type, omega-3. Those fatty acids are essential for human health, but our bodies don’t make them on their own, so we must get them from foods.
What are the claims about seed oils and health?
Critics of seed oils make a range of claims that many scientists say are not borne out by research.
Some critics contend that the way the oils are produced leaves behind toxic byproducts of a chemical called hexane. Hexane is considered hazardous in a gas form, but Decker said the hexane used as a liquid solvent to extract the oil is evaporated off and that the residue that remains “is very low and would not present a risk.”
Another common claim is that the seed oils’ high omega-6 and low omega-3 composition causes an imbalance that may increase the risk of chronic conditions by boosting inflammation in the body.
Belury, who has studied fatty acids for three decades, says that claim is based on an oversimplification and misunderstanding of the science. Studies have shown that increased intake of linoleic acid, the most common omega-6, does not significantly affect concentrations of inflammatory markers in the blood, she said.
“Scientists who study omega-6 and omega-3 think we need both,” Belury said. “Seed oils do not increase acute or chronic inflammation markers.”
In addition, research from the American Heart Association and others has consistently shown that plant-based oils reduce so-called bad cholesterol, lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke, especially compared with sources high in saturated fat.
That’s found in new research from Brigham and Women’s Hospital scientists as well. A study of more than 200,000 adults over more than 30 years released Thursday found that people who ate the highest amounts of butter had a 15% higher risk of dying than those who ate the least. People who ate the most plant-based oils — including seed oils — had a 16% lower risk than those who ate the least.
Dr. Daniel Wang, who led the research, said new modeling data suggests that swapping less than a tablespoon a day of butter for equal calories of plant-based oils could lower premature deaths from cancer and overall mortality by 17%. Such a small daily change could result in “a substantial benefit,” Wang said.
Seed oil consumption has risen
Groups like the Seed Oil Free Alliance, which charges firms to certify their products are free of the oils, note that seed oil consumption in the U.S. has soared in recent decades and that they provide empty calories that “displace other, more nutritious foods.”
Corey Nelson, cofounder of the group, said that just as consumers can buy low-sodium and low-sugar versions of foods, they should be able to choose products that contain no seed oils, if they wish.
Food scientists agree that consumption of seed oils has increased, but they say that’s because they’re widely used in fried and fast foods and ultraprocessed foods, which make up nearly three-quarters of the U.S. food supply. Those foods, which have been linked to a host of health problems, also include high levels of refined grains, added sugars and sodium. There’s no evidence that the seed oils themselves are responsible for poor health outcomes, experts said.
Consumers concerned about seed oils should eat fewer ultraprocessed foods. They should seek medical advice to personalize their consumption of the oils, with people using a variety of oils depending on their health status, Decker said.
Research shows olive oil is the healthiest choice, so people should use it “as their cooking style and pocketbook allows,” he noted. At the same time, they can boost consumption of healthy omega-3s by eating more fish like tuna and salmon.
Both proponents and detractors of seed oils agree on one thing: More nutrition research is needed to explore nuances and resolve long-simmering issues.
In the meantime, scientists said a return to beef tallow, with its high levels of saturated fat, isn’t the answer.
“There is no evidence to indicate that beef tallow is healthier than seed oils,” Decker wrote in an email. “Remember, tallow is also processed to purify the fat.”
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

Lifestyle
Allergy season: How to check pollen levels and alleviate symptoms

ATLANTA (AP) — Allergy season can be miserable for tens of millions of Americans when trees, grass, and other pollens cause runny noses, itchy eyes, coughing and sneezing.
Where you live, what you’re allergic to and your lifestyle can make a big difference when it comes to the severity of your allergies. Experts say climate change is leading to longer and more intense allergy seasons, but also point out that treatments for seasonal allergies have become more effective over the last decade.
Here are some tips from experts to keep allergy symptoms at bay — maybe even enough to allow you to enjoy the outdoors.
Where are pollen levels the worst this year?
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America issues an annual ranking of the most challenging cities to live in if you have allergies, based on over-the-counter medicine use, pollen counts and the number of available allergy specialists.
This year, the top five cities are: Wichita, Kansas; New Orleans; Oklahoma City; Tulsa, Oklahoma; and Memphis.
Which pollens cause allergies?
There are three main types of pollen. Earlier in the spring, tree pollen is the main culprit. After that grasses pollinate, followed by weeds in the late summer and early fall.
Some of the most common tree pollens that cause allergies include birch, cedar, cottonwood, maple, elm, oak and walnut, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America. Grasses that cause symptoms include Bermuda, Johnson, rye and Kentucky bluegrass.
This article is part of AP’s Be Well coverage, focusing on wellness, fitness, diet and mental health. Read more Be Well.
How do I track pollen levels?
Pollen trackers can help you decide when to go outside. The American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology tracks levels through a network of counting stations across the U.S. Counts are available at its website and via email.
Limit your exposure to pollens
The best and first step to controlling allergies is avoiding exposure. Keep the windows in your car and your home closed, even when it’s nice outside.
If you go outside, wearing long sleeves can keep pollen off your skin to help ward off allergic reactions, said Dr. James Baker, an allergist at the University of Michigan. It also provides some sun protection, he added.
When you get home, change your clothes and shower daily to ensure all the pollen is off of you — including your hair. If you can’t wash your hair every day, try covering it when you go outside with a hat or scarf. Don’t get in the bed with your outside clothes on, because the pollen will follow.
It’s also useful to rinse your eyes and nose with saline to remove any pollen, experts said. And the same masks that got us through the pandemic can protect you from allergies — though they won’t help with eye symptoms.
How to relieve allergy symptoms
Over-the-counter nasal sprays are among the most effective treatments for seasonal allergies, experts said.
But the vast majority of patients use them incorrectly, irritating parts of the nose, said Dr. Kathleen Mays, an allergist at Augusta University in Georgia. She suggested angling the nozzle outward toward your ear rather than sticking it straight up your nose.
Over-the-counter allergy pills like Claritin, Allegra and Zyrtec are helpful, but may not be as effective as quickly since they’re taken by mouth, experts said.
Experts also said that if your allergy symptoms are impacting your quality of life, like causing you to lose sleep or a lack focus at work or school, it might be time to consider an allergist appointment for immunotherapies.
Some remedies for allergy relief that have been circulating on social media or suggested by celebrities — like incorporating local honey into your diet to expose yourself to pollen — have been debunked.
Dr. Shayam Joshi, an allergist at Oregon Health and Science University, said that’s because the flowers that bees pollinate typically don’t contain the airborne pollen that causes allergy symptoms.
Is allergy season changing?
With climate change, winters are milder and growing seasons are longer, meaning there’s more opportunity for pollen to stay in the air, resulting in longer and more severe allergy seasons.
In many areas across the country, pollen counts have broken decades of records. In late March, the Atlanta Allergy and Asthma Center measured a pollen count of over 14,000 grains per cubic meter, which is considered extremely high.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Lifestyle
The 250th anniversary of the Battles of Lexington and Concord opens debate over US independence
NEW YORK (AP) — The American Revolution began 250 years ago, in a blast of gunshot and a trail of colonial spin.
Starting with Saturday’s anniversary of the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the country will look back to its war of independence and ask where its legacy stands today.
The semiquincentennial comes as President Donald Trump, the scholarly community and others divide over whether to have a yearlong party leading up to July 4, 2026, as Trump has called for, or to balance any celebrations with questions about women, the enslaved and Indigenous people and what their stories reveal.
The history of Lexington and Concord in Massachusetts is half-known, the myth deeply rooted.
What exactly happened at Lexington and Concord?
Reenactors may with confidence tell us that hundreds of British troops marched from Boston in the early morning of April 19, 1775, and gathered about 14 miles (22.5 kilometers) northwest on Lexington’s town green.
Firsthand witnesses remembered some British officers yelled, “Thrown down your arms, ye villains, ye rebels!” and that amid the chaos a shot was heard, followed by “scattered fire” from the British. The battle turned so fierce that the area reeked of burning powder. By day’s end, the fighting had continued around 7 miles (11 kilometers) west to Concord and some 250 British and 95 colonists were killed or wounded.
But no one has learned who fired first, or why. And the revolution itself was initially less a revolution than a demand for better terms.
Woody Holton, a professor of early American history at the University of South Carolina, says most scholars agree the rebels of April 1775 weren’t looking to leave the empire, but to repair their relationship with King George III and go back to the days preceding the Stamp Act, the Tea Act and other disputes of the previous decade.
“The colonists only wanted to turn back the clock to 1763,” he said.
Stacy Schiff, a Pulitzer Prize winning historian whose books include biographies of Benjamin Franklin and Samuel Adams, said Lexington and Concord “galvanized opinion precisely as the Massachusetts men hoped it would, though still it would be a long road to a vote for independence, which Adams felt should have been declared on 20 April 1775.”
But at the time, Schiff added, “It did not seem possible that a mother country and her colony had actually come to blows.”
A fight for the ages
The rebels had already believed their cause greater than a disagreement between subjects and rulers. Well before the turning points of 1776, before the Declaration of Independence or Thomas Paine’s boast that “We have it in our power to begin the world over again,” they cast themselves in a drama for the ages.
The so-called Suffolk Resolves of 1774, drafted by civic leaders of Suffolk County, Massachusetts, prayed for a life “unfettered by power, unclogged with shackles,” a fight that would determine the “fate of this new world, and of unborn millions.”
The revolution was an ongoing story of surprise and improvisation. Military historian Rick Atkinson, whose “The Fate of the Day” is the second of a planned trilogy on the war, called Lexington and Concord “a clear win for the home team,” if only because the British hadn’t expected such impassioned resistance from the colony’s militia.
The British, ever underestimating those whom King George regarded as a “deluded and unhappy multitude,” would be knocked back again when the rebels promptly framed and transmitted a narrative blaming the royal forces.
“Once shots were fired in Lexington, Samuel Adams and Joseph Warren did all in their power to collect statements from witnesses and to circulate them quickly; it was essential that the colonies, and the world, understand who had fired first,” Schiff said. “Adams was convinced that the Lexington skirmish would be ‘famed in the history of this country.’ He knocked himself out to make clear who the aggressors had been.”
A country still in progress
Neither side imagined a war lasting eight years, or had confidence in what kind of country would be born out of it. The founders united in their quest for self-government but differed how to actually govern, and whether self-government could even last.
Americans have never stopped debating the balance of powers, the rules of enfranchisement or how widely to apply the exhortation, “All men are created equal.”
“I think it’s important to remember that the language of the founders was aspirational. The idea that it was self-evident all men were created equal was preposterous at a time when hundreds of thousands were enslaved,” said Atkinson, who cites the 20th-century poet Archibald MacLeish’s contention that “democracy is never a thing done.”
“I don’t think the founders had any sense of a country that some day would have 330 million people,” Atkinson said. “Our country is an unfinished project and likely always will be.”
Lifestyle
Sweets from the sky! A helicopter marshmallow drop thrills kids in suburban Detroit
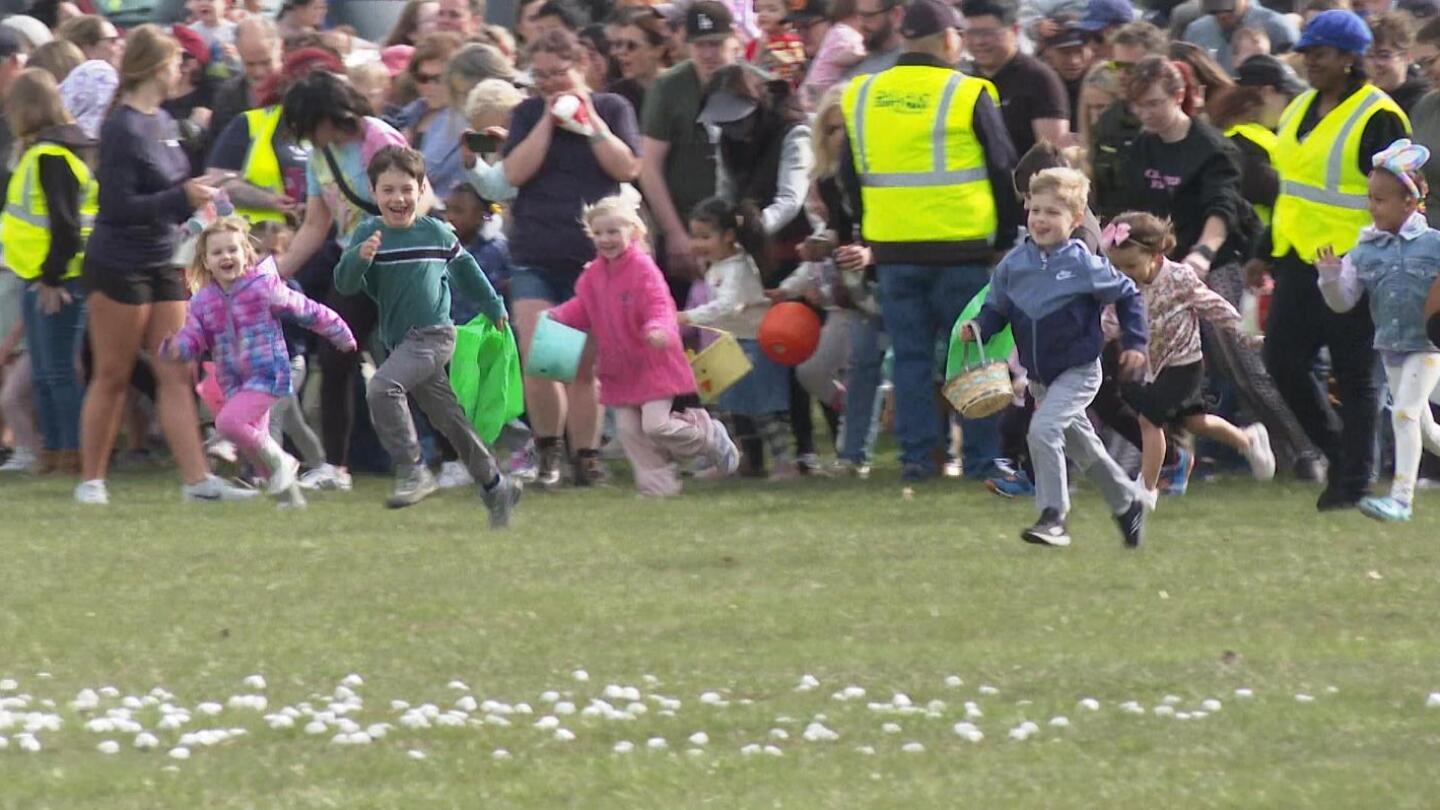

ROYAL OAK, Mich. (AP) — It’s spring in Detroit — warm weather, a few clouds, and a 100% chance of marshmallow downpours.
The source? A helicopter zooming above the green lawn of Worden Park on Friday, unloading sack-fulls of fluffy treats for hundreds of kids waiting eagerly below, some clutching colorful baskets or wearing rabbit ears.
The children cheered and pointed as the helicopter clattered by on its way to the drop zone. Volunteers in yellow vests made sure kids didn’t rush in and start grabbing marshmallows until after the deluge was complete.
For anyone worried about hygiene, don’t fret. The annual Great Marshmallow Drop isn’t about eating the marshmallows — kids could exchange them for a prize bag that included a water park pass and a kite.
The marshmallow drop has been held for over three decades in the Detroit suburb of Royal Oak, Michigan, hosted by Oakland County Parks.
One toddler, Georgia Mason, had no difficulty procuring a marshmallow at her first drop, her dad Matt said.
“Probably the most exciting part was seeing the helicopters. But once we saw the marshmallows drop, we got really excited,” Matt Mason said.
“And, yeah, we joined the melee,” he said, “We managed to get one pretty easy.”
Organizers said 15,000 marshmallows were dropped in all.
The helicopter made four passes, dropping marshmallows for kids in three age categories: 4-year-olds and younger, 5-7-year-olds, and those ages 8 to 12. A drop for kids of all ages with disabilities came later in the day.
“We do it because it’s great for community engagement,” Oakland County recreation program supervisor Melissa Nawrocki said.
“The kids love it,” she continued. “The looks on their faces as they’re picking up their marshmallow and turning in the marshmallow for prizes is great.”
-
 Conflict Zones24 hours ago
Conflict Zones24 hours agoTrump says US may ‘pass’ on helping end war if Russia, Ukraine resist deal | Russia-Ukraine war News
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoAaron Rodgers ‘not holding anybody hostage’ as he decides his future, retirement a possibility
-

 Education1 day ago
Education1 day agoHarvard’s battle with the Trump administration is creating a thorny financial situation
-

 Lifestyle1 day ago
Lifestyle1 day agoSweets from the sky! A helicopter marshmallow drop thrills kids in suburban Detroit
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoLive updates: Trump news, Ukraine peace talks, US immigration, tariffs and university funding
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoNY Rangers’ Panarin, MSG reportedly made settlement payments after employee made sexual assault allegations
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoRussia lifts terror group designation on Afghanistan’s Taliban
-

 Middle East22 hours ago
Middle East22 hours agoDeadly, sombre Good Friday as 58 people killed in Israeli attacks on Gaza | Israel-Palestine conflict News



