Lifestyle
How to help your teenager get enough sleep — and how much they need

Navigating bedtime with a teenager is, in many homes, a nightly battle with a constant refrain: Get off your phone! Go to bed!
Research shows that today’s teenagers are more sleep-deprived than ever before. Adolescents need between eight and 10 hours of sleep, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. But nearly 80% of American teenagers aren’t getting that, and experts say it’s affecting important areas like mental health and school attendance.
Bedtime routines aren’t just for toddlers. Teenagers need them too, says Denise Pope, an expert on child development and a senior lecturer at Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education.
Experts in adolescent sleep say a few small changes to how parents and teens approach sleep can make a dramatic difference.
Try a tech-free bedtime routine for teens
The first step to setting up a better bedtime routine is dealing with technology.
— Separate children from their devices at night. Phones, tablets, streaming services and video games aren’t the only things keeping kids up at night, but experts agree they are a major factor in delaying sleep.
“Get the temptation out of the bedroom,” Pope says. If the phone is within arm’s reach, it’s hard to ignore when notifications buzz. Many teens say they fall asleep while scrolling, or reach for their phone if they have trouble sleeping, and end up scrolling for hours.
— Be prepared for excuses. “My phone is my alarm clock” is something a lot of parents hear. The solution: Buy an alarm clock.
This article is part of AP’s Be Well coverage, focusing on wellness, fitness, diet and mental health. Read more Be Well.
— Put screens away an hour before bedtime. Exposure to light prevents the release of melatonin, the hormone released by the brain that makes us feel drowsy.
Then, replace screens with a new wind-down routine.
— Try to get to bed around the same time each night and start winding down at least 30 minutes before. During that time, silence notifications, take a warm shower, read a book. To get an idea of what your teen’s bedtime should be, try an online “ bedtime calculator,” such as the one from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
— Avoid caffeine and energy drinks in the afternoon and evening.
— The best sleep environment is a cool, dark, quiet room. In noisy households, earplugs and a sleep mask can help. If a bedroom is too warm, it can affect getting to sleep and staying asleep, says adolescent sleep expert Kyla Wahlstrom.
Know the signs of sleep deprivation in teens
Some of the telltale evidence of sleep deprivation: being irritable, grumpy, short-tempered, emotionally fragile, unmotivated, impulsive and more likely to see the world and oneself through a negative lens. A sleep-deprived teen also may fall asleep during the daytime, in the car or in class.
“We often blame adolescents for being lazy or unruly or having bad behavior, much of which could be attributed to the fact that they are chronically sleep-deprived,” says Wendy Troxel, a clinical psychologist who has conducted numerous studies on adolescent sleep.
How do you tell the difference between a sleepy teen and a cranky-but-well-rested one?
— One key sign is what sleep expert Joanna Fong-Isariyawongse calls “zombie mornings.”
“If your teen hits snooze five times, takes forever to get out of bed, asks you for a big cup of coffee first thing in the morning, most likely they are running on empty,” says Fong-Isariyawongse, a neurologist at the University of Pittsburgh.
— Extreme mood swings are another sign. Sleep is critical for emotional processing, which is why sleep-deprived teens are more likely to be irritable, anxious or depressed.
— A sleep-deprived teen may fall behind in school, because sleep is essential for learning and memory consolidation.
— Teens who sleep less are more likely to make bad choices when it comes to drug or alcohol use, drowsy or reckless driving and risky sexual behavior.
— Does your teen sleep until lunchtime on weekends? “Most likely they are not getting enough sleep during the week,” says Fong-Isariyawongse. It’s fine to sleep in a bit, but try to limit it to a couple hours. Otherwise, it throws off the body clock and makes it harder to wake up when the new school week begins.
Why should teenagers care? Show them the science
Explain to your teens why sleep matters, and that it’s not just nagging parents who say so. The data on mental health and sleep is vast.
— Many studies show that depression, anxiety and the risk of suicidal thinking go up as sleep goes down.
— Beyond mood, sleep deprivation affects physical and athletic ability. That’s why several NFL and NBA teams have hired sleep coaches. Teens who are sleep-deprived sustain more physical injuries, because they take more risks, their judgment is impaired, and reflexes and reaction times are not as fast. Teens who get more sleep perform better in sports, and when they do get injuries, they have a quicker recovery time.
— More teenage car accidents come from drowsy driving than driving under the influence of alcohol, studies show. Teens who say they get less than eight hours of sleep a night are more likely to text while driving, not wear a seat belt, drink and drive — or get in a car with a driver who has been drinking.
As any parent knows, telling their teenager to go to sleep does not always work. You need to get their buy-in.
“Kids need to be educated about sleep, and their brain health and emotional health, and how it all ties together,” says Wahlstrom. “Tell your kids, ‘You’ll do better in school, better in sports, you’ll look better after a good night’s sleep.’ Because until they want to help themselves, they won’t do it.”
___
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.
Lifestyle
Allergy season: How to check pollen levels and alleviate symptoms
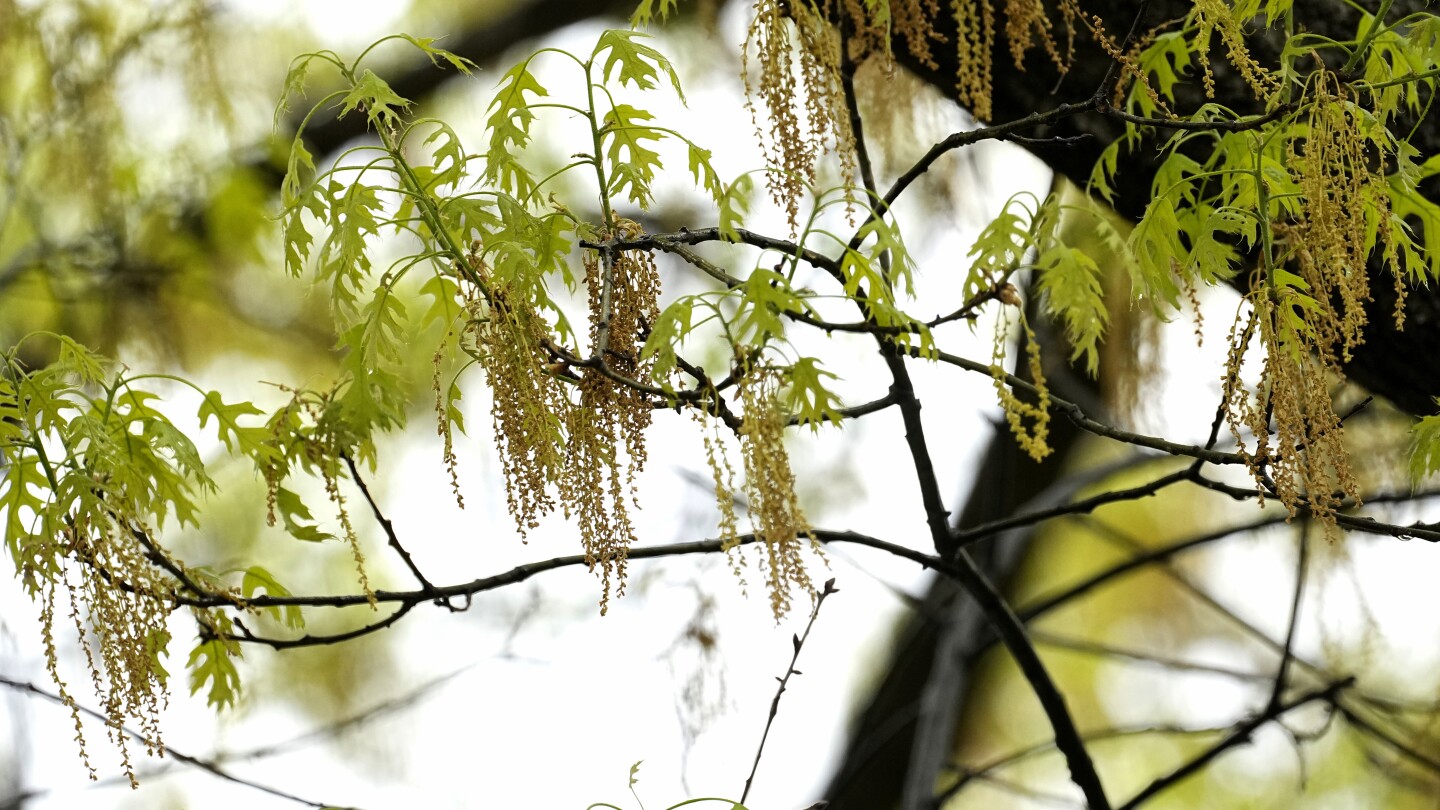

ATLANTA (AP) — Allergy season can be miserable for tens of millions of Americans when trees, grass, and other pollens cause runny noses, itchy eyes, coughing and sneezing.
Where you live, what you’re allergic to and your lifestyle can make a big difference when it comes to the severity of your allergies. Experts say climate change is leading to longer and more intense allergy seasons, but also point out that treatments for seasonal allergies have become more effective over the last decade.
Here are some tips from experts to keep allergy symptoms at bay — maybe even enough to allow you to enjoy the outdoors.
Where are pollen levels the worst this year?
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America issues an annual ranking of the most challenging cities to live in if you have allergies, based on over-the-counter medicine use, pollen counts and the number of available allergy specialists.
This year, the top five cities are: Wichita, Kansas; New Orleans; Oklahoma City; Tulsa, Oklahoma; and Memphis.
Which pollens cause allergies?
There are three main types of pollen. Earlier in the spring, tree pollen is the main culprit. After that grasses pollinate, followed by weeds in the late summer and early fall.
Some of the most common tree pollens that cause allergies include birch, cedar, cottonwood, maple, elm, oak and walnut, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America. Grasses that cause symptoms include Bermuda, Johnson, rye and Kentucky bluegrass.
This article is part of AP’s Be Well coverage, focusing on wellness, fitness, diet and mental health. Read more Be Well.
How do I track pollen levels?
Pollen trackers can help you decide when to go outside. The American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology tracks levels through a network of counting stations across the U.S. Counts are available at its website and via email.
Limit your exposure to pollens
The best and first step to controlling allergies is avoiding exposure. Keep the windows in your car and your home closed, even when it’s nice outside.
If you go outside, wearing long sleeves can keep pollen off your skin to help ward off allergic reactions, said Dr. James Baker, an allergist at the University of Michigan. It also provides some sun protection, he added.
When you get home, change your clothes and shower daily to ensure all the pollen is off of you — including your hair. If you can’t wash your hair every day, try covering it when you go outside with a hat or scarf. Don’t get in the bed with your outside clothes on, because the pollen will follow.
It’s also useful to rinse your eyes and nose with saline to remove any pollen, experts said. And the same masks that got us through the pandemic can protect you from allergies — though they won’t help with eye symptoms.
How to relieve allergy symptoms
Over-the-counter nasal sprays are among the most effective treatments for seasonal allergies, experts said.
But the vast majority of patients use them incorrectly, irritating parts of the nose, said Dr. Kathleen Mays, an allergist at Augusta University in Georgia. She suggested angling the nozzle outward toward your ear rather than sticking it straight up your nose.
Over-the-counter allergy pills like Claritin, Allegra and Zyrtec are helpful, but may not be as effective as quickly since they’re taken by mouth, experts said.
Experts also said that if your allergy symptoms are impacting your quality of life, like causing you to lose sleep or a lack focus at work or school, it might be time to consider an allergist appointment for immunotherapies.
Some remedies for allergy relief that have been circulating on social media or suggested by celebrities — like incorporating local honey into your diet to expose yourself to pollen — have been debunked.
Dr. Shayam Joshi, an allergist at Oregon Health and Science University, said that’s because the flowers that bees pollinate typically don’t contain the airborne pollen that causes allergy symptoms.
Is allergy season changing?
With climate change, winters are milder and growing seasons are longer, meaning there’s more opportunity for pollen to stay in the air, resulting in longer and more severe allergy seasons.
In many areas across the country, pollen counts have broken decades of records. In late March, the Atlanta Allergy and Asthma Center measured a pollen count of over 14,000 grains per cubic meter, which is considered extremely high.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Lifestyle
The 250th anniversary of the Battles of Lexington and Concord opens debate over US independence
NEW YORK (AP) — The American Revolution began 250 years ago, in a blast of gunshot and a trail of colonial spin.
Starting with Saturday’s anniversary of the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the country will look back to its war of independence and ask where its legacy stands today.
The semiquincentennial comes as President Donald Trump, the scholarly community and others divide over whether to have a yearlong party leading up to July 4, 2026, as Trump has called for, or to balance any celebrations with questions about women, the enslaved and Indigenous people and what their stories reveal.
The history of Lexington and Concord in Massachusetts is half-known, the myth deeply rooted.
What exactly happened at Lexington and Concord?
Reenactors may with confidence tell us that hundreds of British troops marched from Boston in the early morning of April 19, 1775, and gathered about 14 miles (22.5 kilometers) northwest on Lexington’s town green.
Firsthand witnesses remembered some British officers yelled, “Thrown down your arms, ye villains, ye rebels!” and that amid the chaos a shot was heard, followed by “scattered fire” from the British. The battle turned so fierce that the area reeked of burning powder. By day’s end, the fighting had continued around 7 miles (11 kilometers) west to Concord and some 250 British and 95 colonists were killed or wounded.
But no one has learned who fired first, or why. And the revolution itself was initially less a revolution than a demand for better terms.
Woody Holton, a professor of early American history at the University of South Carolina, says most scholars agree the rebels of April 1775 weren’t looking to leave the empire, but to repair their relationship with King George III and go back to the days preceding the Stamp Act, the Tea Act and other disputes of the previous decade.
“The colonists only wanted to turn back the clock to 1763,” he said.
Stacy Schiff, a Pulitzer Prize winning historian whose books include biographies of Benjamin Franklin and Samuel Adams, said Lexington and Concord “galvanized opinion precisely as the Massachusetts men hoped it would, though still it would be a long road to a vote for independence, which Adams felt should have been declared on 20 April 1775.”
But at the time, Schiff added, “It did not seem possible that a mother country and her colony had actually come to blows.”
A fight for the ages
The rebels had already believed their cause greater than a disagreement between subjects and rulers. Well before the turning points of 1776, before the Declaration of Independence or Thomas Paine’s boast that “We have it in our power to begin the world over again,” they cast themselves in a drama for the ages.
The so-called Suffolk Resolves of 1774, drafted by civic leaders of Suffolk County, Massachusetts, prayed for a life “unfettered by power, unclogged with shackles,” a fight that would determine the “fate of this new world, and of unborn millions.”
The revolution was an ongoing story of surprise and improvisation. Military historian Rick Atkinson, whose “The Fate of the Day” is the second of a planned trilogy on the war, called Lexington and Concord “a clear win for the home team,” if only because the British hadn’t expected such impassioned resistance from the colony’s militia.
The British, ever underestimating those whom King George regarded as a “deluded and unhappy multitude,” would be knocked back again when the rebels promptly framed and transmitted a narrative blaming the royal forces.
“Once shots were fired in Lexington, Samuel Adams and Joseph Warren did all in their power to collect statements from witnesses and to circulate them quickly; it was essential that the colonies, and the world, understand who had fired first,” Schiff said. “Adams was convinced that the Lexington skirmish would be ‘famed in the history of this country.’ He knocked himself out to make clear who the aggressors had been.”
A country still in progress
Neither side imagined a war lasting eight years, or had confidence in what kind of country would be born out of it. The founders united in their quest for self-government but differed how to actually govern, and whether self-government could even last.
Americans have never stopped debating the balance of powers, the rules of enfranchisement or how widely to apply the exhortation, “All men are created equal.”
“I think it’s important to remember that the language of the founders was aspirational. The idea that it was self-evident all men were created equal was preposterous at a time when hundreds of thousands were enslaved,” said Atkinson, who cites the 20th-century poet Archibald MacLeish’s contention that “democracy is never a thing done.”
“I don’t think the founders had any sense of a country that some day would have 330 million people,” Atkinson said. “Our country is an unfinished project and likely always will be.”
Lifestyle
Sweets from the sky! A helicopter marshmallow drop thrills kids in suburban Detroit
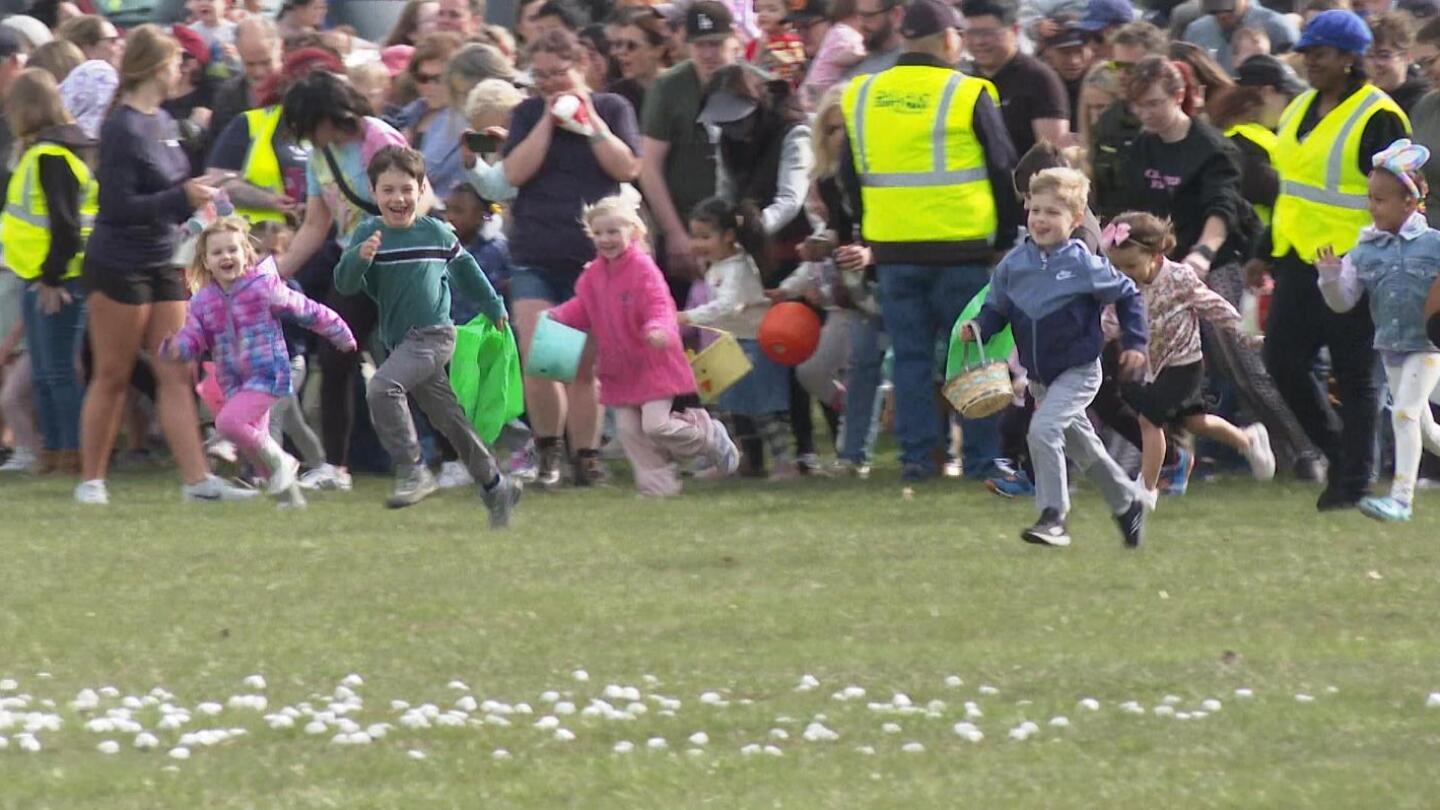

ROYAL OAK, Mich. (AP) — It’s spring in Detroit — warm weather, a few clouds, and a 100% chance of marshmallow downpours.
The source? A helicopter zooming above the green lawn of Worden Park on Friday, unloading sack-fulls of fluffy treats for hundreds of kids waiting eagerly below, some clutching colorful baskets or wearing rabbit ears.
The children cheered and pointed as the helicopter clattered by on its way to the drop zone. Volunteers in yellow vests made sure kids didn’t rush in and start grabbing marshmallows until after the deluge was complete.
For anyone worried about hygiene, don’t fret. The annual Great Marshmallow Drop isn’t about eating the marshmallows — kids could exchange them for a prize bag that included a water park pass and a kite.
The marshmallow drop has been held for over three decades in the Detroit suburb of Royal Oak, Michigan, hosted by Oakland County Parks.
One toddler, Georgia Mason, had no difficulty procuring a marshmallow at her first drop, her dad Matt said.
“Probably the most exciting part was seeing the helicopters. But once we saw the marshmallows drop, we got really excited,” Matt Mason said.
“And, yeah, we joined the melee,” he said, “We managed to get one pretty easy.”
Organizers said 15,000 marshmallows were dropped in all.
The helicopter made four passes, dropping marshmallows for kids in three age categories: 4-year-olds and younger, 5-7-year-olds, and those ages 8 to 12. A drop for kids of all ages with disabilities came later in the day.
“We do it because it’s great for community engagement,” Oakland County recreation program supervisor Melissa Nawrocki said.
“The kids love it,” she continued. “The looks on their faces as they’re picking up their marshmallow and turning in the marshmallow for prizes is great.”
-

 Education1 day ago
Education1 day agoHarvard’s battle with the Trump administration is creating a thorny financial situation
-

 Lifestyle2 days ago
Lifestyle2 days agoThousands of pilgrims trek through New Mexico desert to historic adobe church for Good Friday
-

 Middle East14 hours ago
Middle East14 hours agoTunisian court hands opposition figures lengthy jail terms | Human Rights News
-
 Conflict Zones1 day ago
Conflict Zones1 day agoTrump says US may ‘pass’ on helping end war if Russia, Ukraine resist deal | Russia-Ukraine war News
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoTrump’s ‘lone ranger’: How Steve Witkoff became the defacto point man on America’s foreign policy challenges
-

 Lifestyle1 day ago
Lifestyle1 day agoSweets from the sky! A helicopter marshmallow drop thrills kids in suburban Detroit
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoAaron Rodgers ‘not holding anybody hostage’ as he decides his future, retirement a possibility
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoManchester United pulls off ‘miracle’ Europa League victory against Lyon




