Middle East
‘A shocking breach’: Trump officials leak Yemen attack plans in Signal chat | Donald Trump News
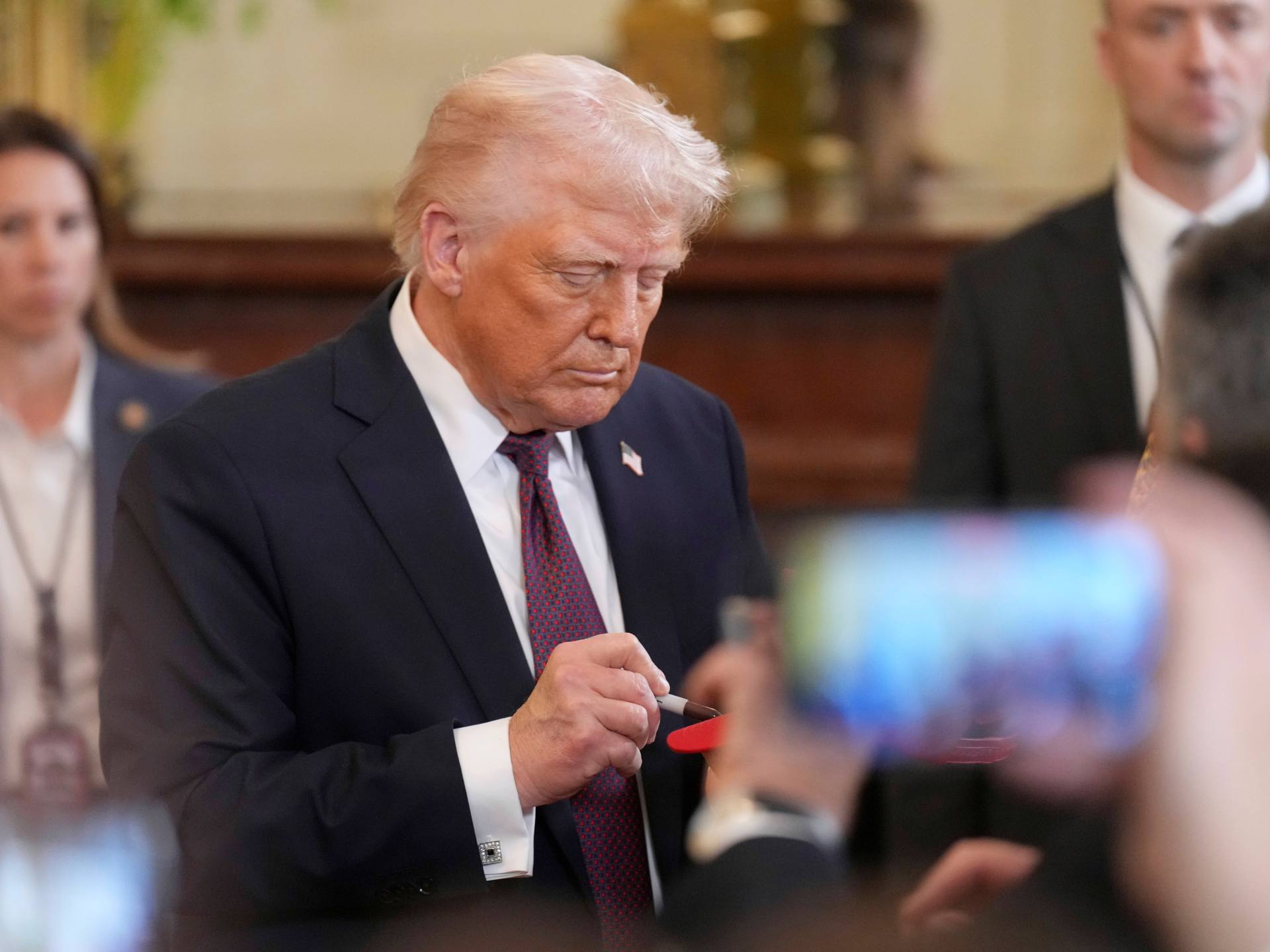

The administration of United States President Donald Trump has confirmed that a journalist from The Atlantic magazine was included in a private social media chat about upcoming attacks on the Houthi armed group in Yemen.
On Monday, The Atlantic published an article from editor-in-chief Jeffrey Goldberg, in which he described the stunning realisation that he had been added to a group chat where high-level government officials were discussing military actions.
“The world found out shortly before 2 p.m. eastern time [18:00 GMT] on March 15 that the United States was bombing Houthi targets across Yemen,” Goldberg wrote in the opening lines of his article.
“I, however, knew two hours before the first bombs exploded that the attack might be coming. The reason I knew this is that Pete Hegseth, the secretary of defense, had texted me the war plan at 11:44 a.m [15:44 GMT].”
Goldberg explained that he received a messaging request from a user named “Michael Waltz” on the encrypted messaging app Signal. At first, he doubted that this Waltz could be the real Michael Waltz, Trump’s national security adviser.
But soon, he found himself in the midst of a conversation with 18 government officials, some of whom appeared to be Secretary of State Marco Rubio, Vice President JD Vance and Hegseth.
“I have never seen a breach quite like this,” Goldberg wrote. He ultimately notified the White House about the security breach and removed himself from the chat.
The Trump administration has confirmed the incident in a statement from the National Security Council that was shared with the media.
“At this time, the message thread that was reported appears to be authentic, and we are reviewing how an inadvertent number was added to the chain,” council spokesperson Brian Hughes said in the statement.
“The thread is a demonstration of the deep and thoughtful policy coordination between senior officials.”
At a news conference later on Monday, State Department spokesperson Tammy Bruce declined to comment, referring reporters to the White House.
Trump was likewise pressed on the scandal during a White House event to unveil a steel mill for the automaker Hyundai in Louisiana.
“I don’t know anything about it,” Trump began, before taking a swipe at the magazine itself.
“I’m not a big fan of The Atlantic. To me, it’s a magazine that’s going out of business. I think it’s not much of a magazine, but I know nothing about it.”
He proceeded to ask reporters to give him details about the security breach.
“What were they talking about?” Trump asked. He then appeared to confuse the breach with an intentional attempt to subvert the US military operation in Yemen.
“It couldn’t have been very effective because the attack was very effective. I can tell you that,” Trump said. “I don’t know anything about it. You’re telling me about it for the first time.”
But critics are already calling for an investigation into what occurred. Senator Chris Coons, a Democrat from Delaware, was among those who said Congress should hold an oversight hearing and demand accountability.
“Jeffrey Goldberg’s reporting in The Atlantic calls for a prompt and thorough investigation,” Coons wrote on social media.
“If senior advisors to President Trump in fact used non-secure, non-government systems to discuss and convey detailed war plans, it’s a shocking breach of the standards for sharing classified information that could have put American servicemembers at risk.”

What happened?
The latest wave of US attacks against the Houthis came on March 15, after Trump announced on social media that he had ordered the military “to launch decisive and powerful” actions against the Yemeni group.
But Goldberg’s interactions with the private Signal chat offer a glimpse at how that decision came about.
The Houthis have long been the subject of US military action, including under Trump’s predecessor, Democrat Joe Biden.
Since October 2023, the Houthis have attacked Israeli vessels and commercial ships in the Red Sea and surrounding waterways, as a means of protesting against Israel’s war in Gaza.
Approximately 100 merchant ships have come under Houthi fire from that point onwards, and two have been sunk. However, the Houthi attacks came to a halt in January, when a short-lived ceasefire took hold in Gaza.
Still, Trump announced early in his second term that he would designate the Houthis a “foreign terrorist organisation”, an action that was fulfilled earlier this month.
Then, on March 2, Israel began to block humanitarian aid from reaching Gaza, which lacks adequate food and medical supplies. In response, the Houthis warned they would attack if the blockade was not ended. The ceasefire in Gaza has since disintegrated, leading to further death and destruction in the Palestinian territory.
It was March 11 when Goldberg said he received his invitation from Waltz, the national security adviser, on Signal.
“It immediately crossed my mind that someone could be masquerading as Waltz in order to somehow entrap me,” Goldberg wrote in The Atlantic.
“I accepted the connection request, hoping that this was the actual national security adviser, and that he wanted to chat about Ukraine, or Iran, or some other important matter.”
Two days later, Goldberg instead found himself part of a private chat entitled, “Houthi PC small group”. There, some of the most senior officials in the US government appeared to be discussing an imminent attack on Houthi strongholds in Yemen, including the capital Sanaa.
“I had very strong doubts that this text group was real,” Goldberg explained. “I also could not believe that the national security adviser to the president would be so reckless as to include the editor in chief of The Atlantic in such discussions with senior U.S. officials, up to and including the vice president.”
The access, however, granted Goldberg a front-row seat to some of the back-room haggling unfolding in the Trump administration – and some of the policy schisms those discussions reveal.
A participant in the chat who appeared to be Vice President Vance expressed concern that attacking the Houthis would ultimately benefit European trade more than US shipping interests.
He proposed delaying the bombing campaign, in order to better gauge public opinion and the economic ramifications.
“I am willing to support the consensus of the team and keep these concerns to myself,” Vance said. “But there is a strong argument for delaying this a month, doing the messaging work on why this matters, seeing where the economy is, etc.”
A person identified as Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth responded that a delay would “not fundamentally change the calculus”. Nevertheless, he warned against the US dragging its feet.
“Immediate risks on waiting: 1) this leaks, and we look indecisive; 2) Israel takes an action first – or Gaza cease fire falls apart – and we don’t get to start this on our own terms,” Hegseth wrote.

Vance appeared resigned, his concerns most focused on the benefits any strikes might have for Europe.
“If you think we should do it let’s go. I just hate bailing Europe out again,” Vance replied.
Hegseth again chimed in, “VP: I fully share your loathing of European free-loading. It’s PATHETIC. But Mike is correct, we are the only ones on the planet (on our side of the ledger) who can do this.”
Another official, identified as SM, appeared to chime in on behalf of the president. Goldberg said he assumed this to be Stephen Miller, Trump’s homeland security adviser.
“The president was clear: green light, but we soon make clear to Egypt and Europe what we expect in return,” SM wrote.
“If the US successfully restores freedom of navigation at great cost there needs to be some further economic gain extracted in return.”
Goldberg declined to provide the operational details of the military strike that unfolded afterwards. But he did explain that the actions outlined in the group chat matched the bombs raining down in Yemen.
He also shared the jubilation that followed the military strikes: officials sharing emojis of the US flag, a flame and a flexing bicep.
“The Signal chat group, I concluded, was almost certainly real. Having come to this realization, one that seemed nearly impossible only hours before, I removed myself from the Signal group,” Goldberg wrote.
He questioned the legality of US officials discussing such sensitive military action on a social media platform.
“It is not uncommon for national-security officials to communicate on Signal. But the app is used primarily for meeting planning and other logistical matters – not for detailed and highly confidential discussions of a pending military action,” Goldberg explained.
“Had they lost their phones, or had they been stolen, the potential risk to national security would have been severe.”
The editor also questioned whether the officials on the chat were violating public records law. The messages in the chat were set to automatically delete after a certain period of time.
“Text messages about official acts are considered records that should be preserved,” Goldberg wrote.
Waltz himself could be in legal jeopardy for reportedly including Goldberg in the first place – thereby leaking national security information into the public sphere.
“The group was transmitting information to someone not authorized to receive it,” Goldberg said. “That is the classic definition of a leak.”
Middle East
Lebanese president says disarming Hezbollah ‘delicate’ as Israel kills two | Israel attacks Lebanon News
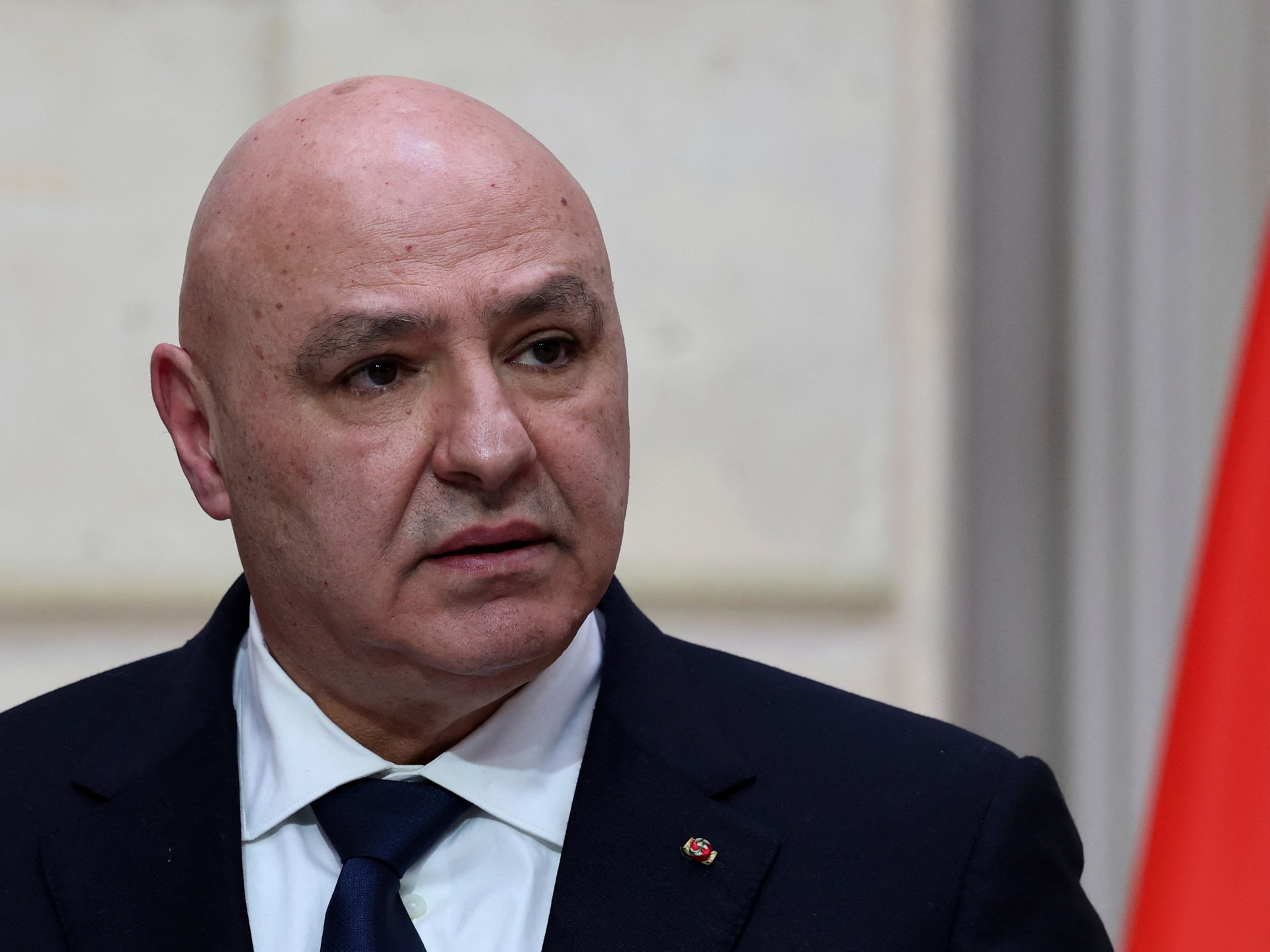

Joseph Aoun makes the comment as the Lebanese army says it foils a rocket attack on Israel.
Lebanese President Joseph Aoun says he will not be rushed to disarm Hezbollah under unfavourable circumstances as the Israeli military continues to launch deadly air strikes on the country in violation of a November ceasefire.
In comments to reporters after a meeting with a Maronite patriarch to mark Easter on Sunday, the former army chief said he considers disarming the Iran-aligned group a “sensitive, delicate issue” that must be handled with consideration to preserve national peace.
“Any controversial domestic issue in Lebanon can only be approached through conciliatory, nonconfrontational dialogue and communication. If not, we will lead Lebanon to ruin,” Aoun said.
The Trump administration has been applying sustained pressure on Beirut to push for the disarming of Hezbollah, leading to Aoun announcing last week that he hopes to complete the process by the end of 2025 – the first time a senior official has set any deadline.
Aoun’s comments on Sunday came shortly after the Lebanese government praised the army for foiling an imminent attack on Israel, a first since the November ceasefire with Hezbollah, which Israel has violated on numerous occasions.
The Lebanese army released images of confiscated rockets and launch pads and said it arrested multiple individuals previously involved in rocket attacks on Israel as well.
The raid that led to the confiscated munitions was reported to have taken place in the Sidon area of southern Lebanon.
The office of Prime Minister Nawaf Sharif urged security forces to “thwart suspicious plots that seek to embroil Lebanon in further wars” and said this work proves that the Lebanese state is moving towards full sovereignty over its territory with its own forces.
“The Lebanese state alone is the authority that makes decisions regarding war and peace and is the body authorised to possess weapons,” he said.
Hezbollah has not immediately reacted to Sunday’s statements, but its leader Naim Qassem said on Friday that the group “will not let anyone disarm” it, especially as the Israeli military continues to occupy parts of southern Lebanon.
Hezbollah was formed in the aftermath of the Israeli invasion of Lebanon in 1982 and grew over the decades to possess substantial political and military power. This included forcing Israel out from its occupation of southern Lebanon in 2000 and fighting Israel to a stalemate in a 2006 war.
But the organisation has lost many leaders in Israeli assassinations as well as much military equipment since the start of Israel’s war on Gaza in October 2023 and must withdraw its military forces from southern Lebanon as part of the ceasefire.
Israeli air strikes kill two
Lebanon’s Ministry of Public Health said on Sunday that two people were killed in two Israeli air raids in southern Lebanon.
Israeli warplanes fired at least two missiles at a house in Hula, a village in Nabatieh governorate, killing one person, the ministry said.
An Israeli drone attack also targeted a vehicle in Kaoutariyet as-Siyad, killing another person, it said.
The footage below, which has been verified by Al Jazeera’s Sanad fact-checking agency, shows plumes of smoke rising after Israeli air strikes targeted the heights of the Iqlim al-Tuffah region of southern Lebanon.
مراسل الجديد: سلسلة غارات عنيفة من الطيران الحربي إستهدفت أطراف مليتا ومرتفعات إقليم التفاح@farhat_muhamad1 pic.twitter.com/8TMHLdc06q
— Al Jadeed News (@ALJADEEDNEWS) April 20, 2025
The Israeli military said one of its strikes on southern Lebanon killed a deputy head of a Hezbollah unit responsible for smuggling weapons and funds to the group, including across the country’s border with Syria.
The army added that the targeted man was “extensively involved” in Hezbollah efforts to revitalise after the group took heavy blows during the war.
After killing two other people on Saturday, the Israeli army also claimed they were Hezbollah members.
Middle East
The Hawaii of Israel: How Trump legitimised a longstanding Israeli vision | Israel-Palestine conflict

On April 7, United States President Donald Trump met Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu for a second time since his inauguration. Speaking to the media, Trump doubled down on his earlier comments about the Gaza Strip, describing it as an “incredible piece of important real estate”.
Trump also repeated his suggestion that the Palestinians should leave the Strip “to different countries” and claimed that people “really do love that vision. … A lot of people like my concept.”
Days later, about 70 percent of Gaza had been turned into a “no-go zone” for Palestinians. Confirming that Israel is working “in accordance with the US president’s vision, which we seek to realise”, Israeli Defence Minister Israel Katz declared Israel’s intention to “seize” more territory, adding that “wilful passage” will be given to Palestinians who want to leave.
It is by now clear that Trump’s statements on Gaza have had the effect of legitimising a longstanding Israeli vision of ethnic cleansing of the Strip. What the US president calls “my concept” is in fact not his at all.
Over decades of Israeli occupation and colonisation of the Gaza Strip, there have been multiple plans to empty out or disperse the Palestinian population in a bid to secure full control over this part of Palestine. The power of colonial practices has also been tested. For example, to draw Israeli settlers and thereby help transform Gaza’s demographics, the Strip was at one point even promoted as the “Hawaii of Israel”.
Left out of Israeli war aims in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the Gaza Strip emerged out of the 1949 Armistice Agreements under Egyptian military rule. Constituting only a small part of what until then had been the Gaza District of Palestine, the Gaza Strip was home to two groups of Palestinians: the local population and refugees – people who had been forced off their land as Israel expanded its territorial reach during the war.
As the guns fell silent, the Gaza Strip became known in Israeli policy circles as the “job unfinished” – a slice of land next to the Egyptian border that Israel’s leaders would like to control, preferably without its Palestinian population.
Israel’s first attempt to take Gaza by force occurred in 1956. But under pressure from US President Dwight Eisenhower, Israeli Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion had no choice but to withdraw and put an end to the Israeli occupation. The botched attempt taught Israel an important lesson: To redraw the map of the Middle East and to make its territorial expansionist agenda a success, Israel needed American support and approval.
The 1967 Arab-Israeli War was far more successful in this regard. Through conquest and occupation, the Gaza Strip was brought under direct Israeli rule. This opened the door to revitalise “transfer” – the forced displacement and ethnic cleansing of Palestinians. Seen as both necessary and permissible or, in Ben-Gurion’s words, “an important humane and Zionist idea”, transfer was recognised as an effective tool to advance Zionist colonisation of Palestine.
In the following years, as noted by Palestinian historian Nur Masalha, transfer acquired different labels. These included “population exchange”, “Arab return to Arabia”, “voluntary emigration” and “rehabilitation” with different Israeli governments taking different approaches.
One approach was Defence Minister Moshe Dayan’s “open bridges”, which allowed Palestinians in Gaza to leave for other countries in search of work. Another was to open offices in Gaza’s refugee camps to organise and pay for travel and passports for Palestinians willing to “voluntarily migrate”, which in effect turned the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs into a “global travel agency”. Regardless of the approach, Israel’s policy objective remained the same: to create a drive in Palestinians to leave the Strip.
“I want them all to go, even if they go to the moon,” Israeli Prime Minister Levi Eshkol said. Expressing Israeli frustration, Eshkol articulated the feeling of being stuck with what was considered the problem of Gaza. After all, only the Palestinian population there – and the sizeable refugee population in particular – stood in the way of full Israeli annexation.
In response to Israel’s Gaza “dilemma”, its politicians also looked for more comprehensive solutions. This led to an almost continuous flow of plans for the “rehabilitation” of Palestinians outside the Strip. Starting immediately after the 1967 war, a variety of potential destinations came up. These included the West Bank, the Sinai Peninsula, Iraq, or even as far afield as Canada and Australia.
Despite Israeli efforts and elaboration of plans – and much to the disappointment of Israel’s decision-makers – the initiatives came to naught as the number of Palestinians leaving the Strip remained limited. And given other considerations, including moral, legal and diplomatic ones, the plans to displace a large number of Palestinians from Gaza were left in the drawer.
But as Israeli politicians turned to examine their menu of choices in the post-October 7, 2023, era, “voluntary emigration”, or forced displacement, re-emerged. Gone was any sensitivity to international opinion and potential reactions. Instead, Trump has led the way, making statements on Gaza that in effect turn decades of Zionist ideology and practice into official American policy.
By means of his policy stance, the US president has legitimised a longstanding Israeli vision of ethnic cleansing in the Strip. In the process, his articulation of policy has moved ever closer to the strand of Revisionist Zionism that viewed Palestinians as aliens in their own land and, therefore, “transferable”.
In arguing that Palestinians need to go to make Israel and the region safe, Trump has departed from the internationally shared principle that Palestinians in the Gaza Strip – as elsewhere in the occupied Palestinian territory – have legitimate rights to self-determination in their land. As such, Trump brings to mind Revisionist Zionist ideologue Ze’ev Jabotinsky, who argued that “when the Arab claim is confronted with our Jewish demand to be saved, it is like the claims of appetite vs the claims of starvation” with “transfer” inextricably linked to Jewish rights to the land.
The cynical promises of a better future for people who are left with nothing but their land after a brutal war of erasure and plausible genocide must be taken seriously. The legitimacy Trump has given to Israeli plans poses a threat in the here and now, but it could also outlast his presidency.
That is because he has offered US presidential sanction of ethnic cleansing as an acceptable tool. This leaves the door open for Israel – in the near or distant future – to pursue “transfer”, “rehabilitation” and “voluntary emigration” of Palestinians, whether in Gaza or the West Bank.
Furthermore, the American president has repeatedly communicated US support for illegal land seizures and colonisation. Suggesting Gaza (and Greenland) could become “US territory”, he has reintroduced and validated ideas that most leaders of the world had put on the scrap heap of history.
Finally, Trump has shifted the US position away from the premise of working towards a two-state solution. In fact, considering his statements, there appears to be a fundamental disregard for Palestinians in Gaza and their collective right to self-determination.
Looking at current US policy against historical record, Trump’s “Riviera of the Middle East” seems a curious combination of Zionist ethnic cleansing under the “transfer” model and the colonial ideal of the “Hawaii of Israel”.
It is no wonder Trump has been cheered on by Israeli leaders as he calls for the forced depopulation of the Gaza Strip and its transformation into fully fledged colonial territory – annexed or otherwise. After all, Trump’s ideas follow in the footsteps of Zionist leaders from Ben-Gurion to Netanyahu, under whom transfer has been the preferred but diplomatically and legally challenging option all along.
With Trump going out in front, such challenges could turn into tomorrow’s opportunities. It remains the task of other states to stand up against Israeli-American normalisation of continued ethnic cleansing and colonial land grabs in Palestine.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera’s editorial stance.
Middle East
Everything you need to know about Iran-US nuclear negotiations | Features
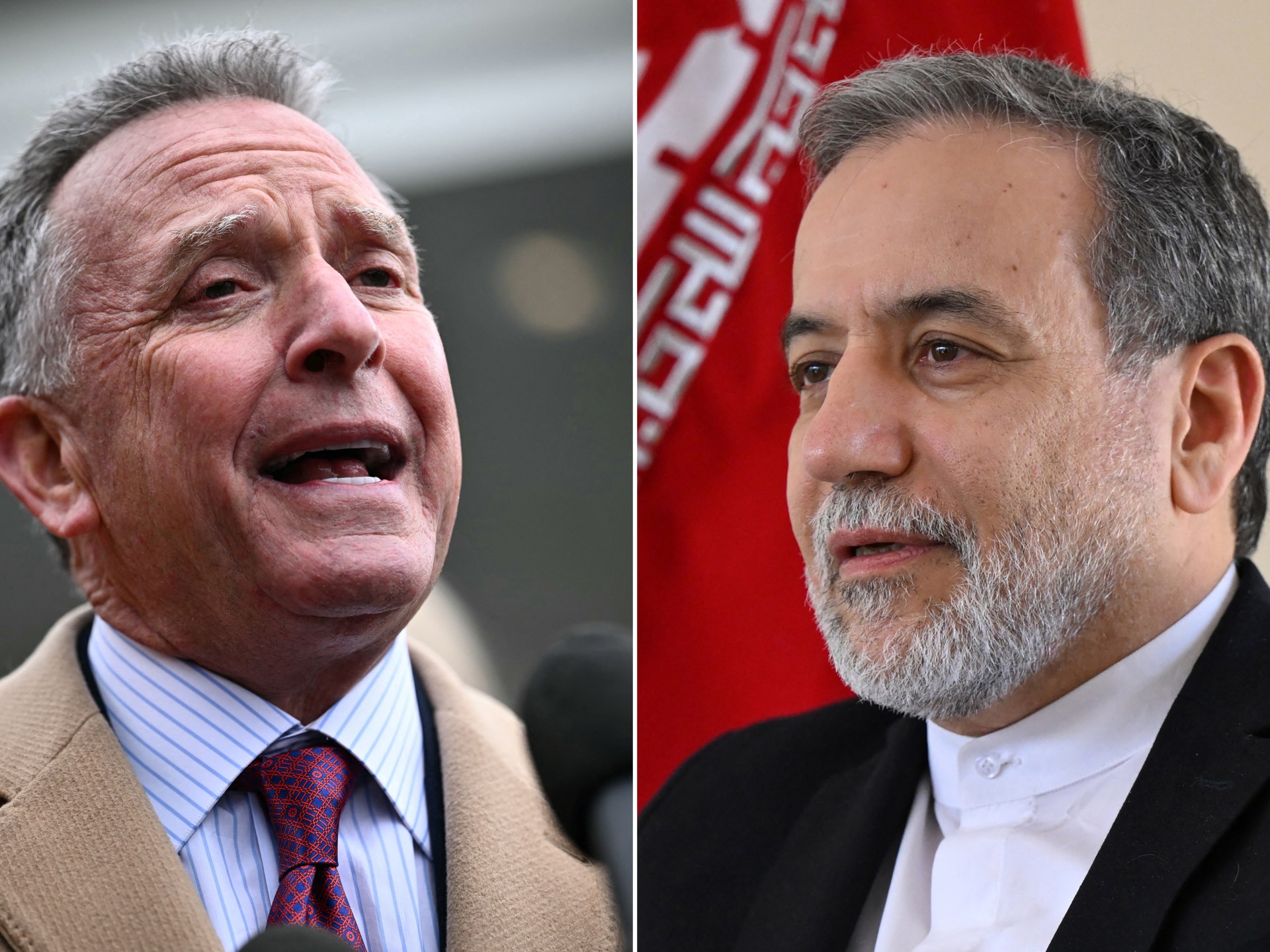

Iran and the United States held “constructive” discussions over the Iranian nuclear programme.
The second round of Oman-mediated talks in Rome took place on Saturday, a week after the first session in Muscat, the Omani capital.
“Technical discussions” are now expected to begin on Wednesday in Oman, after which more high-level meetings will be held to move closer to an agreement.
So, what are these technical discussions? And is an agreement likely?
Here’s what you need to know:
What are these technical talks?
On Wednesday, working-level experts from both sides will begin discussing the inner workings of sanctions relief and how that relates to Iran’s nuclear programme.
The sanctions regimes imposed on Iran are complex and multilayered, and each layer has to be linked to a specific action or guarantee Iran is being asked to undertake with regard to its nuclear programme.
Three days after these talks, another round of high-level talks will be held in Muscat.
The last two rounds were indirect talks between Iran’s Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi and US Special Envoy Steve Witkoff, passing messages through Omani Foreign Minister Badr Albusaidi.

How did we get here?
Officials are optimistic about the progress on talks that started with US President Donald Trump threatening Tehran with attacks if it did not negotiate.
In early March, Trump said he had written to Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, asking for talks on the country’s nuclear programme.
But the letter was sent via the United Arab Emirates, and UAE presidential diplomatic adviser Anwar Gargash delivered it nearly a week after Trump’s announcement.
After saying Trump’s letter had not been received yet, Khamenei declared Iran would not accept the “demands” of “bully governments”.
But something thawed in the normally icy relations, and Iran agreed to indirect talks after Omani mediation.
Interestingly, Oman was also the mediator for the initial secret talks between Iran and the US that led to the JCPOA.

Does Iran want a nuclear weapon?
Iran has given no indication that it plans to build a nuclear weapon. In fact, the supreme leader has issued a religious decree years ago prohibiting the pursuit of such a weapon.
When Trump’s threats escalated, Khamenei said if Iran chooses to pursue a nuclear weapon, nobody could stop it. However, he has not reversed his decree prohibiting it.
Wasn’t there a deal limiting Iran’s nuclear programme already?
There was. The 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) was a diplomatic win for former US President Barack Obama’s administration.
Under the terms of the deal, Iran committed to regular inspections of its nuclear energy programme in return for relief on some Western sanctions.
However, criticising the agreement during his first term, Trump withdrew from the JCPOA in May 2018 and imposed punitive sanctions on Iran.

What does the US want exactly?
One thing that has come up in discussions is how much enriched uranium Iran has and at what level.
Enriched uranium is used for nuclear energy reactors, but that is usually enriched to between 3 and 5 percent.
According to the International Atomic Energy Agency, Iran has 274.8kg (605.8 pounds) of uranium enriched up to 60 percent, lower than the 90 percent enrichment needed for a weapon.
Under the JCPOA, Iran could enrich uranium up to 3.67 percent and keep a uranium stockpile of 300kg (661 pounds).
Witkoff has said 3.67 percent would be an acceptable level of uranium enrichment, which is the same as agreed on in the JCPOA under Obama.

So, why does Trump want another deal?
It is hard to read Trump’s mind.
But going by what he has said, he sees himself as a dealmaker willing to talk to anyone, even if he ends up with a deal similar to the last one.
He was supposedly influenced by Israel’s opinion when he said the JCPOA was a “bad deal” and left it in 2018.
Israel has long seen Iran as a foe, claiming it is secretly pursuing a bomb and is a bigger regional threat than Israel’s increasingly violent occupation of Palestine.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu was so invested that he dedicated part of his 2012 UN General Assembly address to drawing a cartoon bomb with “red lines” through it, to illustrate his point.
Since international inspections began, there has been consensus that Iran was sticking to the deal, although it has increased its enrichment levels since Trump’s withdrawal from the JCPOA.
So, is there going to be a deal?
It is too early to say.
There are promising signs, such as reports that the Iranian and US teams were in the same room for at least part of the second round of negotiations, and the progress made in technical talks.
Araghchi, according to the semiofficial Tasnim news agency, said: “We succeeded in reaching a better understanding on certain principles and goals.”
He posted on Saturday that “for now, optimism may be warranted but only with a great deal of caution”.
Iran has insisted that the US guarantee it will adhere to this agreement. For its part, the US has insisted that Iran halt the uranium enrichment it claims is necessary to run its nuclear energy programme.

-

 Conflict Zones2 days ago
Conflict Zones2 days ago‘How do I live like this?’ asks Gaza boy who lost arms in Israeli attack | Gaza News
-
 Conflict Zones2 days ago
Conflict Zones2 days agoTrump says US may ‘pass’ on helping end war if Russia, Ukraine resist deal | Russia-Ukraine war News
-

 Middle East1 day ago
Middle East1 day agoTunisian court hands opposition figures lengthy jail terms | Human Rights News
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoRussia sentences 19-year-old woman to nearly three years in a penal colony after poetic anti-war protest
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoVance, Vatican officials engage in ‘exchange of opinions’ over migrants
-

 Africa1 day ago
Africa1 day agoUnprecedented trial for apartheid atrocities opens in South Africa
-

 Europe1 day ago
Europe1 day agoTrump administration ready to recognize Russian control of Crimea as part of framework to end Ukraine war, source says
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoRory McIlroy could go onto win 10 majors now Masters ‘shackles are off,’ says men’s captain of his hometown golf club




