Africa
France: seven-year sentence and fine suggested for Sarkozy over Libya financing deal

French prosecutors on Thursday requested a seven-year prison sentence and a 300,000-euro (around $325,000) fine for former President Nicolas Sarkozy, in connection with allegations that his 2007 presidential campaign was illegally financed by former Libyan leader Moammar Gadhafi’s government.
The National Financial Prosecutor’s Office, known by its French acronym PNF, also called for a five-year ban on Sarkozy’s civic, civil and family rights — a measure that would bar him from holding elected office or serving in any public judicial role.
The case, which opened in January and is expected to conclude on April 10, is considered the most serious of the multiple legal scandals that have clouded Sarkozy’s post-presidency.
The 70-year-old Sarkozy, who led France from 2007 to 2012, faces charges of passive corruption, illegal campaign financing, concealment of embezzlement of public funds and criminal association. He has denied any wrongdoing.
The accusations trace back to 2011, when a Libyan news agency and Gadhafi himself said that the Libyan state had secretly funneled millions of euros into Sarkozy’s 2007 campaign.
In 2012, the French investigative outlet Mediapart published what it said was a Libyan intelligence memo referencing a 50 million-euro funding agreement. Sarkozy denounced the document as a forgery and sued for defamation.
French magistrates later said that the memo appeared to be authentic, though no conclusive evidence of a completed transaction has been presented.
Investigators also looked into a series of trips by Sarkozy’s associates to Libya between 2005 and 2007.
In 2016, Franco-Lebanese businessman Ziad Takieddine told Mediapart that he had delivered suitcases filled with cash from Tripoli to the French Interior Ministry under Sarkozy. He later retracted his statement. That reversal is now the focus of a separate investigation into possible witness tampering.
Sarkozy and his wife, Carla Bruni-Sarkozy, have both been placed under preliminary investigation in that case.
Sarkozy’s former ministers Claude Guéant, Brice Hortefeux, and Éric Woerth are also on trial, along with eight other defendants. But prosecutors have made clear the central figure is the former president himself — accused of knowingly benefiting from a “corruption pact” with a foreign dictatorship while campaigning to lead the French republic.
While Sarkozy has already been convicted in two other criminal cases, the Libya affair is widely seen as the most politically explosive — and the one most likely to shape his legacy.
In December 2024, France’s highest court upheld his conviction for corruption and influence peddling, sentencing him to one year of house arrest with an electronic bracelet. That case stemmed from tapped phone calls uncovered during the Libya investigation. In a separate ruling in February 2024, a Paris appeals court found him guilty of illegal campaign financing in his failed 2012 reelection bid.
Sarkozy has dismissed the Libya allegations as politically motivated and rooted in forged evidence. But if convicted, he would become the first former French president found guilty of accepting illegal foreign funds to win office.
A verdict is expected later this year.
Africa
Ivory Coast opposition call for election reform ahead of vote
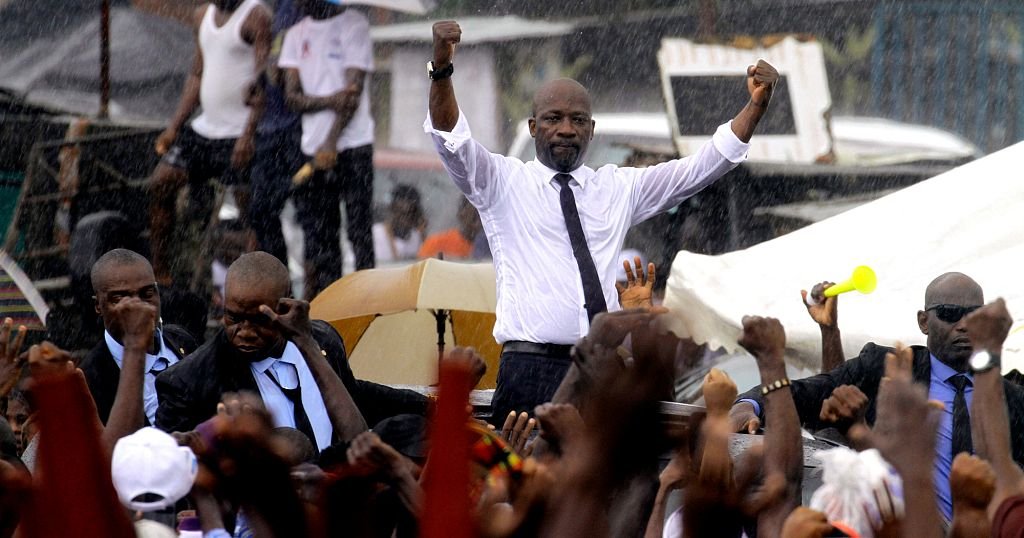
The Ivory Coast’s political opposition, an alliance of parties known as the Coalition for a Peaceful Alternation, called on Saturday for political dialogue with the ruling party, Rally of the Republicans (RDR), five months ahead of the presidential election.
Opposition leaders denounced President Alassane Ouattara’s potential candidacy, as well as the exclusion of several political figures from the electoral list, including banker Tidjane Thiam, former chief executive officer (CEO) of Swiss bank Credit Suisse. To allow the candidacy of all political leaders, the country’s former First Lady, Simone Gbagbo asked President Alassane Ouattara “to take his pen to write an amnesty law that will erase everything”.
In Paris, Tidjane Thiam, president of the coalition and the PDCI, the main opposition party, projected a video onto big screens. In the video, he said that “justice must not be instrumentalized” and called for a revision of the electoral lists before the election.
The coalition strongly criticizes the Independent Electoral Commission, considering it biased. The presidential election in Côte d’Ivoire is scheduled for October 25, 2025. The Coalition for a Peaceful Alternation (known as CAP) in Ivory Coast was formed on March 10, 2025, to confront the presidential majority bloc. It brings together a number of opposition figures, including former political figures such as Pascal Affi N’Guessan, Charles Blé Goudé, and former First Lady Simone Gbagbo.
Alassane Ouattara became president of Côte d’Ivoire in May 2011 following the 2010 presidential election. That election was marked by a violent post-election crisis that pitted Ouattara’s supporters against those of outgoing President Laurent Gbagbo.
Since taking power, Ouattara has served three presidential terms, and his potential candidacy for a fourth term has drawn fierce criticism from the opposition. However, his supporters argue that the new constitution, passed in 2016, resets the clock.
Africa
DR Congo Justice Minister under fire over $19M transfer
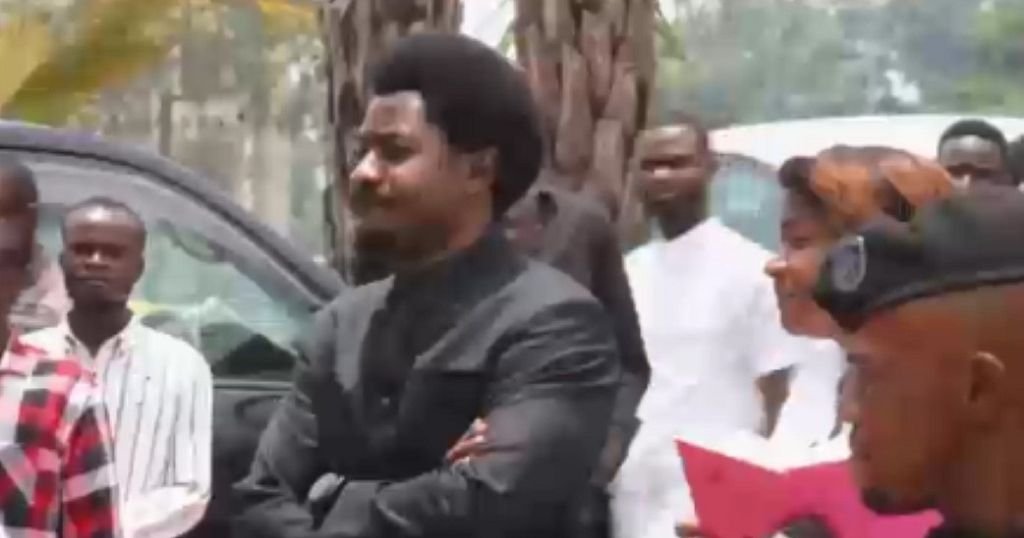

In the Democratic Republic of Congo, pressure is mounting on Justice Minister Constant Mutamba after explosive allegations over a multi-million dollar no-bid contract and suspicious fund transfers.
On Tuesday, lawmakers grilled the Attorney General for six hours and Mutamba for five. The focus: a $29 million deal awarded without competition, and a $19 million payment to Zion Construction—wired just one day after the company opened its bank account.
The funds didn’t come from the state treasury, but from FRIVAO, the agency managing $325 million in war reparations from Uganda. That agency falls under Mutamba’s direct authority. Defending himself, the minister admitted to “errors” and asked for forgiveness—but claimed he’s the target of political revenge.
He also blamed tensions with Prime Minister Judith Suminwa for a toxic work climate. Lawmakers say the accusations are serious, and the judiciary must be allowed to act. Mutamba’s future in government now hangs in the balance.
Africa
Global Heat Report: Climate change fuels silent killer

Four billion people, about half the world’s population, experienced at least one extra month of extreme heat due to human-caused climate change from May 2024 to May 2025, scientists say. The extreme heat caused illness, death, crop losses, and strained energy and healthcare systems, according to the analysis from World Weather Attribution, Climate Central and the Red Cross. “Although floods and cyclones often dominate headlines, heat is arguably the deadliest extreme event,” the report said.
Many heat-related deaths are unreported or are mislabeled by comorbid conditions like heart disease or kidney failure. Heat waves are silent killers, said Friederike Otto, associate professor of climate science at Imperial College London, one of the report’s authors. “People don’t fall dead on the street in a heat wave … people either die in hospitals or in poorly insulated homes and therefore are just not seen.” Low income communities and vulnerable populations, such as older adults and people with medical conditions, suffer the most from extreme heat.
The scientists used peer-reviewed methods to study how much climate change boosted temperatures in a heat wave and calculated how much more likely its occurrence was due to climate change. In almost all countries in the world, the number of extreme heat days has at least doubled. The report says strategies to prepare for heat waves include monitoring and reporting systems for extreme temperatures, providing emergency health services, cooling shelters, updated building codes, enforcing heat safety rules at work, and designing cities to be more heat-resilient.
While these strategies help people adapt to the increasingly frequent and severe heat waves, “only comprehensive mitigation, through phasing out of fossil fuels, will limit the severity of future heat-related harms,” the study said.
-

 Africa4 days ago
Africa4 days agoSurvivor of Liverpool car ramming talks of shock and panic
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoThe Knicks are bringing hope and title dreams back to New York after years in the doldrums
-

 Lifestyle3 days ago
Lifestyle3 days agoChildren and careers: Talking to kids about what they want to be when they grow up
-

 Lifestyle4 days ago
Lifestyle4 days agoHow to decorate a patio, balcony or other small outdoor space
-

 Lifestyle4 days ago
Lifestyle4 days agoFaizan Zaki hopes to go from spelling bee runner-up to champ
-

 Middle East5 days ago
Middle East5 days agoHajj pilgrimage in Saudi Arabia to begin on June 4 | Religion News
-

 Middle East4 days ago
Middle East4 days agoGaza’s aid system isn’t broken. It’s working exactly as designed | Humanitarian Crises
-

 Europe5 days ago
Europe5 days agoMacron’s marital shove disappears from French airwaves




