Education
Trump signs executive order to dismantle the Education Department
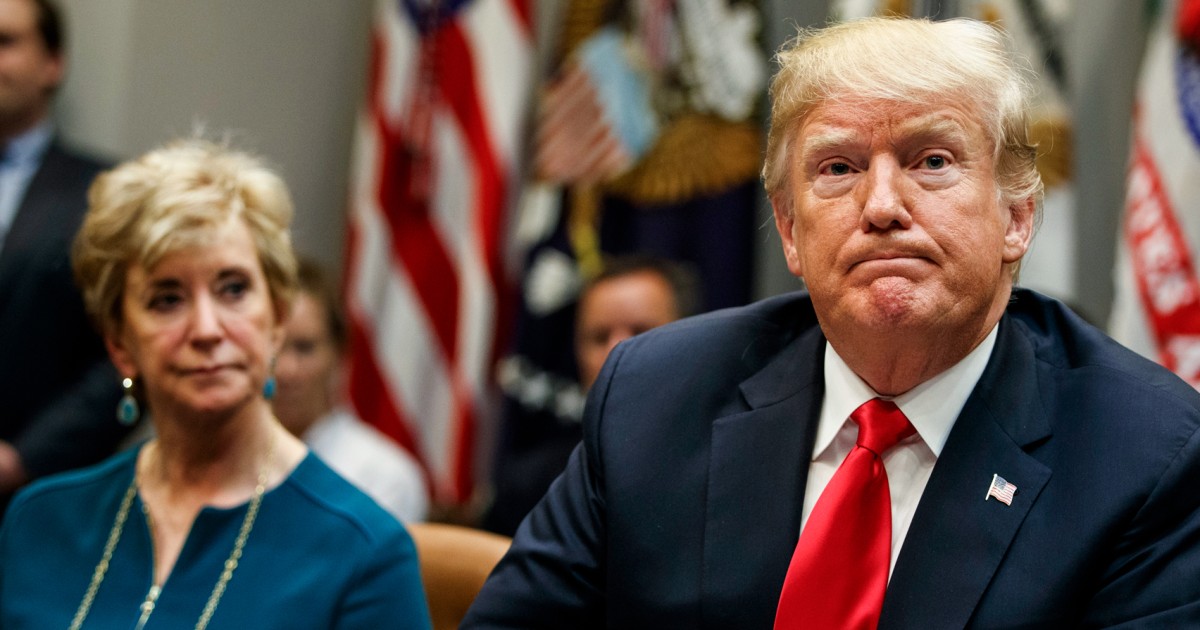

WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump signed an executive order Thursday directing Education Secretary Linda McMahon to start dismantling the Department of Education.
“It sounds strange, doesn’t it? Department of Education. We’re going to eliminate it,” Trump said while speaking in the East Room of the White House at a ceremony where he was flanked by children seated at school desks. Before signing the order, Trump turned to the children and asked, “Should I do this?”
Introducing McMahon, Trump said that “hopefully she will be our last secretary of education.” He vowed “to find something else for you, Linda.”
Congressional approval would be needed to fully abolish the department. Trump said that he hoped Democrats would vote in favor of legislation to do that.
“I hope they’re going to be voting for it,” Trump said of congressional Democrats, “because ultimately it may come before them.”
Immediately after the signing, Sen. Bill Cassidy, R-La., the chair of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee said in a post on X that he will “submit legislation” to accomplish Trump’s goal of shutting down the Department of Education “as soon as possible.”
Congress established the Department of Education in 1979 during President Jimmy Carter’s administration, and any effort to abolish the department would face major obstacles from Democrats in the Republican-controlled Senate, where 60 votes are required to overcome a filibuster and advance a measure to a final vote.
The House Education Committee’s top Democrat, Rep. Bobby Scott, D-Va., called the executive order “reckless” and argued it would put “low-income students, students of color, students with disabilities, and rural students at risk.”
White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt told reporters Thursday morning that the department would not be completely eliminated under the executive order, saying its “critical functions” would continue, including the enforcement of civil rights laws and oversight of student loans and Pell grants.
“The Department of Education will be much smaller than it is today,” Leavitt said, adding that the order directed McMahon “to greatly minimize the agency. So when it comes to student loans and Pell grants, those will still be run out of the Department of Education.”
Follow live politics coverage here
The executive order also will not affect department activities aimed at meeting the educational needs of students with disabilities or Title I funding, which goes to school districts with a high proportion of students from low-income families, a senior administration official told NBC News on Wednesday.
The text of the order was not immediately published after the White House signing ceremony, where several Republican state attorneys general and governors were in attendance. Trump publicly acknowledging Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton and others.
Polling on eliminating the Department of Education shows the move is broadly unpopular, due in large part to opposition from Democrats and independents. A Quinnipiac survey conducted March 6-10 found that 60% of registered voters opposed the plan, while 33% were in favor of it. Among Democrats, just 1% are in favor of the move, while 98% oppose it. The survey had a margin of error of plus or minus 2.8 percentage points.
At her Senate confirmation hearing last month, McMahon acknowledged the need to coordinate with Congress to close the department.
“Certainly President Trump understands that we’ll be working with Congress,” she said in response to a question from Cassidy. “We’d like to do this right. We’d like to make sure that we are presenting a plan that I think our senators could get on board with and our Congress could get on board with that would have a better functioning Department of Education, but certainly does require congressional action.”
With Trump’s executive order, however, it appears the administration to some extent is sidestepping lawmakers. McMahon said on SiriusXM’s “The David Webb Show” on Tuesday that as they “wind down” her department, administration officials want to ensure they are providing states with best practices and the tools they will need.
In her justification for eliminating the department, McMahon added, “I think it’s important to note what the Department of Education does not do. The Department of Education doesn’t educate anyone. It doesn’t hire teachers. It doesn’t establish curriculum. It doesn’t hire school boards or superintendents. It really is to help provide funding so that the states themselves can help with their own programs. But that creativity and innovation has to come from the state level.”
McMahon and the administration have already taken steps in recent weeks to gut the department by cutting the workforce nearly in half.
NBC News recently reported that state officials and lawmakers have said they’re not prepared to take on the full responsibility of education policy, and Trump’s latest order will likely be met with more legal challenges.
Labor and civil rights groups issued statements Wednesday blasting the administration for the move. National Education Association President Becky Pringle said Wednesday that the administration’s actions “will hurt all students by sending class sizes soaring, cutting job training programs, making higher education more expensive and out of reach for middle class families, taking away special education services for students with disabilities, and gutting student civil rights protections.”
NAACP President Derrick Johnson called the order “unconstitutional,” adding that “the rule of law doesn’t seem to matter” to Trump.
“Only Congress can establish or abolish an executive agency,” Johnson said. “Trump is not just seeking to shut down an agency, he is deliberately dismantling the basic functions of our democracy, one piece at a time. This is a dark day for the millions of American children who depend on federal funding for a quality education, including those in poor and rural communities with parents who voted for Trump.”
Education
Judge orders detained Tufts student Rumeysa Öztürk to be transferred back to Vermont
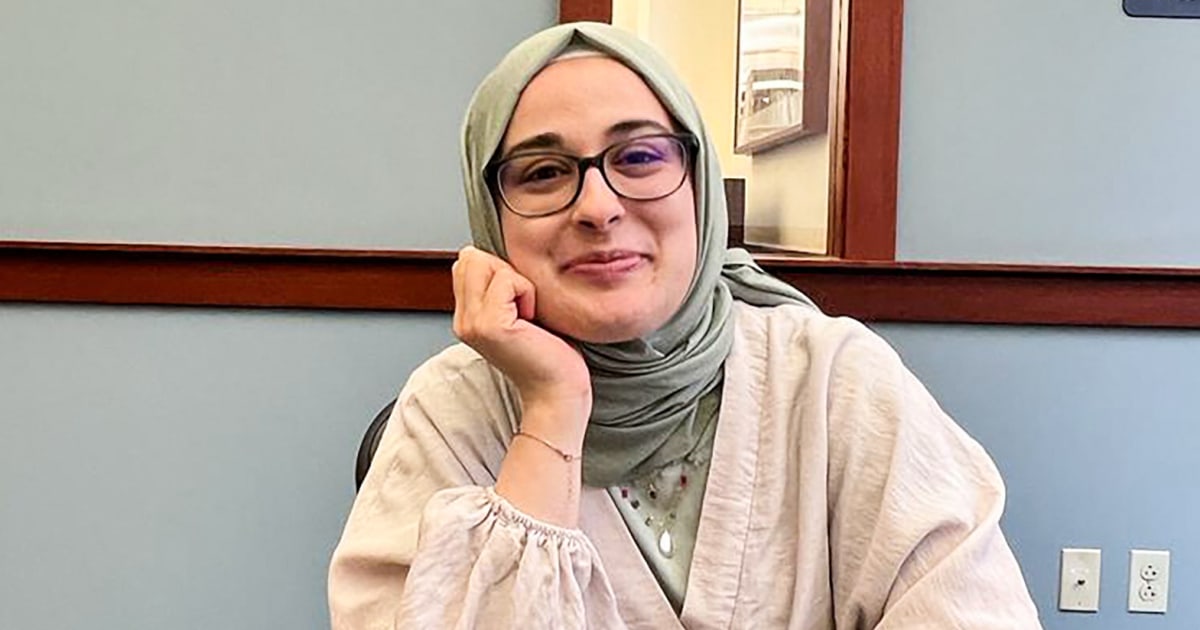

A federal judge on Friday ordered that the Tufts University student who wrote an essay about Israel and the war in Gaza and is now fighting deportation must be transferred back to Vermont.
Judge William K. Sessions III stayed his order for four days to give the government a chance to appeal.
Rumeysa Öztürk, a 30-year-old Turkish national in the United States on a visa, is being held at an Immigration and Customs Enforcement detention center in Louisiana.
In Friday’s ruling, the judge refused efforts by the government to dismiss her habeas petition.
He found that Öztürk “has raised significant constitutional concerns with her arrest and detention.”
The Tufts doctoral student was arrested March 25 in Somerville, Massachusetts, and the Department of Homeland Security has accused her of engaging “in activities in support of Hamas.”
She co-wrote an opinion essay in 2024 for the student newspaper that called on Tufts to “acknowledge the Palestinian genocide,” which the undergraduate student government had demanded in a resolution.
The essay criticized university leadership for its response to the student government’s resolutions that it “disclose its investments and divest from companies with direct or indirect ties to Israel.”
“A university op-ed advocating for human rights and freedom for the Palestinian people should not lead to imprisonment,” one of her attorneys, Mahsa Khanbabai, said Friday. “Our immigration laws should not be manipulated to rip people away from their homes and their loved ones.”
Öztürk’s attorneys called Friday’s ruling a victory, and said that the federal government was trying to manipulate where her case would be heard so that it could try for its preferred outcome.
Friday’s ruling allows Öztürk to remain in ICE custody in Vermont while her habeas petition, which challenges her detainment, proceeds in federal court, as well as her removal case in immigration court in Louisiana.
The Department of Justice declined to comment Friday.
Öztürk is one of a number of international students in the U.S. on visas who the Trump administration is trying to deport for their actions protesting the conduct of Israel in its war against Hamas in Gaza, which it launched after the Hamas attacks on Israel on Oct. 7, 2023.
Tufts University has defended Öztürk and has petitioned that she be released from custody. The university said the opinion essay did not violate its policies and was in accordance with its position on free speech.
“The University has no further information suggesting that she has acted in a manner that would constitute a violation of the University’s understanding of the Immigration and Naturalization Act,” the university leadership said in a declaration earlier this month.
Education
Harvard’s battle with the Trump administration is creating a thorny financial situation
Harvard’s brewing conflict with the Trump administration could come at a steep cost — even for the nation’s richest university.
On April 14, Harvard University President Alan Garber announced the institution would not comply with the administration’s demands, including to “audit” Harvard’s students and faculty for “viewpoint diversity.” The federal government, in response, froze $2.2 billion in multi-year grants and $60 million in multi-year contracts with the university.
According to CNN and multiple other news outlets, the Trump administration has now asked the Internal Revenue Service to revoke Harvard’s tax-exempt status. If the IRS follows through, it would have severe consequences for the university. The many benefits of nonprofit status include tax-free income on investments and tax deductions for donors, education historian Bruce Kimball told CNBC.
Bloomberg estimated the value of Harvard’s tax benefits in excess of $465 million in 2023.
Nonprofits can lose their tax exemptions if the IRS determines they are engaging in political campaign activity or earning too much income from unrelated activities. Few universities have lost their non-profit status. One of the few examples was Christian institution Bob Jones University, which lost its tax exemption in 1983 for racially discriminatory policies.
White House spokesperson Harrison Fields told the Washington Post that the IRS started investigating Harvard before President Donald Trump suggested on Truth Social that the university should be taxed as a “political entity.” The Treasury Department did not reply to a request for comment from CNBC.
A Harvard spokesperson told CNBC that the government has “no legal basis to rescind Harvard’s tax exempt status.”
“The government has long exempted universities from taxes in order to support their educational mission,” the spokesperson wrote in a statement. “Such an unprecedented action would endanger our ability to carry out our educational mission. It would result in diminished financial aid for students, abandonment of critical medical research programs, and lost opportunities for innovation. The unlawful use of this instrument more broadly would have grave consequences for the future of higher education in America.”
The federal government has challenged Harvard on yet another front, with the Department of Homeland Security threatening to stop international students from enrolling. The Student and Exchange Visitor Program is administered by Immigration and Customs Enforcement, which falls under the DHS.
International students make up more than a quarter of Harvard’s student body. However, Harvard is less financially dependent on international students than many other U.S. universities as it already offers need-based financial aid to international students in its undergraduate program. Many other universities require international students to pay full tuition.
The Harvard spokesperson declined to comment to CNBC on whether the university would sue the administration over the federal funds or any other grounds. Lawyers Robert Hur of King & Spalding and William Burck of Quinn Emanuel are representing Harvard, stating in a letter to the federal government that its demands violate the First Amendment.
Harvard, the nation’s richest university, has more resources than other academic institutions to fund a long legal battle and weather the storm. However, its massive endowment — which has raised questions during the recent developments — is not a piggy bank.
Why Harvard’s endowment is so large
Harvard has an endowment of nearly $52 billion, averaging $2.1 million in endowed funds per student, according to a study by the National Association of College and University Business Officers, or NACUBO, and asset manager Commonfund.
That size makes it larger than than the GDP of many countries.
The endowment generated a 9.6% return last fiscal year, which ended June 30, according to the university’s latest annual report.
Founded in 1636, Harvard has had more time to accumulate assets as the nation’s oldest university. It also has robust donor base, receiving $368 million in gifts to the endowment in 2024. While the university noted that more than three-quarters of the gifts averaged $150 per donor, Harvard has a history of headline-making donations from ultra-rich alumni.
Kimball, emeritus professor of philosophy and history of education at the Ohio State University, attributes the outsized wealth of elite universities like Harvard to a willingness to invest in riskier assets.
University endowments were traditionally invested very conservatively, but in the early 1950s Harvard shifted its allocation to 60% equities and 40% bonds, taking on more risk and creating the opportunity for more upside.
“Universities that didn’t want to assume the risk fell behind,” Kimball told CNBC in March.
Other universities soon followed suit, with Yale University in the 1990s pioneering what would become the “Yale Model” of investing in alternative assets like hedge funds and natural resources. Though it proved lucrative, only universities with large endowments could afford to take on the risk and due diligence that was needed to succeed in alternative investments, according to Kimball.
According to Harvard’s annual report, the largest chunks of the endowment are allocated to private equity (39%) and hedge funds (32%). Public equities constitute another 14% while real estate and bonds/TIPs make up 5% each. The remainder is divided between cash and other real assets, including natural resources.
The university has made substantial portfolio allocation changes over the past seven years, the report notes. The Harvard Management Company has cut the endowment’s exposure to real estate and natural resources from 25% in 2018 to 6%. These cuts allowed the university to increase its private equity allocation. To limit equity exposure, the endowment has upped its hedge fund investments.
The endowment is not a piggy bank
University endowments, though occasionally staggering in size, are not slush funds. The pools are actually made up of hundreds or even thousands of smaller funds, the majority of which are restricted by donors to be dedicated to areas including professorships, scholarships or research.
Harvard has some 14,600 separate funds, 80% of which are restricted to specific purposes including financial aid and professorships. Last fiscal year, the endowment distributed $2.4 billion, 70% of which was subject to donors’ directives.
“Most of that money was put in for a specific purpose,” Scott Bok, former chairman of the University of Pennsylvania, told CNBC in March. “Universities don’t have the ability to break open the proverbial piggy bank and just grab the money in whatever way they want.”
Some of these restrictions are overplayed, according to former Northwestern University President Morton Schapiro.
“It’s true that a lot of money is restricted, but it’s restricted to things you’re going to spend on already like need-based aid, study abroad, libraries,” Bok said previously.
How Harvard is shoring up its finances
Harvard has $9.6 billion in endowed funds that are not subject to donor restrictions. The annual report notes that “while the University has no intention of doing so,” these assets “could be liquidated in the event of an unexpected disruption” under certain conditions.
Liquidating $9.6 billion in assets, nearly 20% of total endowed funds, would come at the cost of future cash flow, as the university would have less to invest.
Harvard did not respond to CNBC’s queries about increasing endowment spending. Like most universities, it aims to spend around 5% of its endowment every year. Assuming the fund generates high-single-digit investment returns, spending just 5% allows the principal to grow and keep pace with inflation.
For now, Harvard is taking a hard look at its operating budget. In mid-March, the university started taking austerity measures, including a temporary hiring pause and denying admission to graduate students waitlisted for this upcoming fall.
Harvard is also issuing $750 million in taxable bonds due September 2035. This past February, the university issued $244 million in tax-exempt bonds. A slew of universities including Princeton and Colgate are also raising debt this spring.
So far, Moody’s has not updated its top-tier AAA rating for Harvard’s bonds. However, when it comes to higher education as a whole, the ratings agency isn’t so optimistic, lowering its outlook to negative in March.
Education
Trump admin threatens to stop Harvard from enrolling foreign students

The Trump administration is continuing its battle against Harvard University — this time, canceling $2.7 million in grants and threatening to stop the enrollment of international students.
Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem on Wednesday announced the cancellation of two DHS grants to the school, declaring it “unfit to be entrusted with taxpayer dollars.”
Noem also said she sent a letter to Harvard demanding “detailed records” on foreign student visa holders’ “illegal and violent activities” by April 30.
If Harvard does not meet that deadline, it’ll immediately lose its Student and Exchange Visitor Program certification, she warned.
The release alleged Harvard’s foreign visa holders participated in riots and spewed antisemitic hate targeting Jewish students following the Hamas incursion against Israel on Oct. 7, 2023.
“If Harvard cannot verify it is in full compliance with its reporting requirements, the university will lose the privilege of enrolling foreign students,” a DHS news release said.
The two canceled grants were: an $800,303 grant for Implementation Science for Targeted Violence Prevention, which Noem said “branded conservatives as far-right dissidents in a shockingly skewed study,” and a $1.9 million Blue Campaign Program Evaluation and Violence Advisement grant that Noem alleged “funded Harvard’s public health propaganda.”
“Harvard bending the knee to antisemitism — driven by its spineless leadership — fuels a cesspool of extremist riots and threatens our national security,” Noem said in a statement. “With anti-American, pro-Hamas ideology poisoning its campus and classrooms, Harvard’s position as a top institution of higher learning is a distant memory. America demands more from universities entrusted with taxpayer dollars.”
It’s the latest punch by the Trump administration against the nation’s most prestigious university.
Earlier this week, the Trump administration announced that it would freeze more than $2 billion in grants to Harvard after the institution refused to accept demands that included auditing the viewpoints of its student body. Trump has also called for Harvard to lose its tax-exempt status.
On Monday, Harvard University’s lawyers sent a letter rejecting a list of demands from the Trump administration. In a statement posted online, Harvard President Alan Garber referred to the demands as “an attempt to control the Harvard community” and vowed to fight back.
A Harvard spokesperson told NBC News on Thursday that the school will “not surrender its independence or relinquish its constitutional rights,” while complying with the law.
-

 Conflict Zones2 days ago
Conflict Zones2 days agoHaiti in ‘free fall’ as violence escalates, rights group warns | Armed Groups News
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoPalestinian photographer Samar Abu Elouf wins world’s top photo prize | Gaza News
-

 Africa2 days ago
Africa2 days agoEuropean Union announces new asylum measures
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoJu Wenjun: Chinese grandmaster makes history by winning fifth Women’s World Chess Championship
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoHamas accuses Israel of weaponising aid as Gaza’s hunger crisis worsens | Gaza News
-

 Lifestyle2 days ago
Lifestyle2 days agoPicking a team from bars to beam and hoping for 10s: Fantasy leagues in gymnastics are a thing
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoPortrait of amputee Palestinian boy from Gaza wins World Press Photo award | Israel-Palestine conflict News
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoArsenal reaches first Champions League semifinal in 16 years, with Inter Milan also advancing



