Conflict Zones
Russia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 1,166 | Russia-Ukraine war News
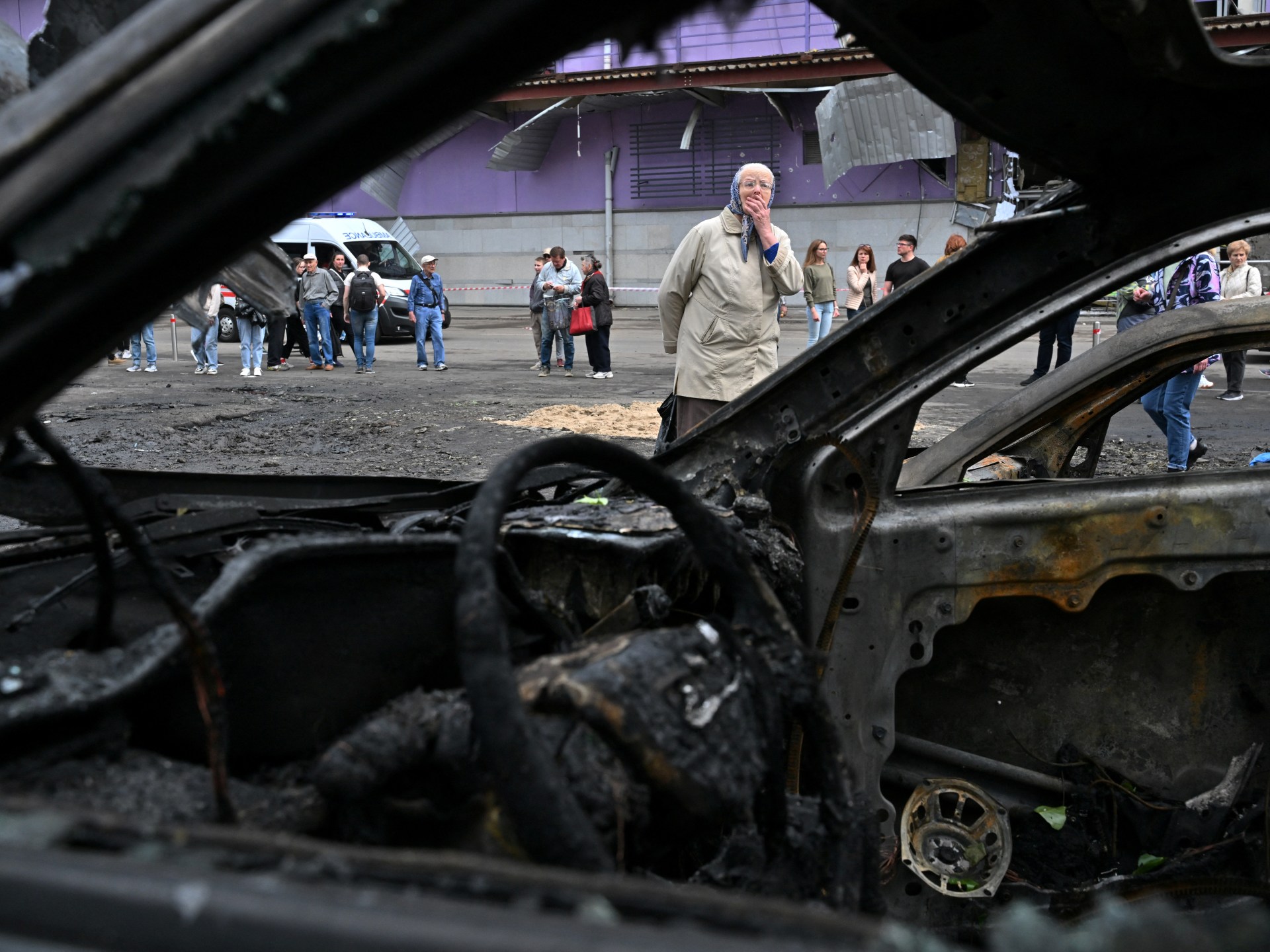

These are the key events on day 1,166 of Russia’s war on Ukraine.
Here is where things stand on Monday, May 5:
Fighting
Russian forces repelled four drones flying towards Moscow, the capital’s mayor, Sergei Sobyanin, said in a post on Telegram. There were no initial reports of damage or casualties, Sobyanin said, adding that emergency services were working at the scene.
Ukrainian forces attacked a factory in Russia’s Bryansk region, destroying much of the plant, Governor Alexander Bogomaz said on Telegram. There were no casualties, Bogomaz said.
Russian forces destroyed 13 Ukrainian drones overnight over Russia’s Rostov, Belgorod and Bryansk regions, Moscow’s Ministry of Defence said on Sunday.
A Russian drone attack injured at least 11 people, including two children, in Kyiv’s Obolonskyi and Sviatoshynskyi districts, Timur Tkachenko, the head of the Kyiv City Military Administration, said on social media.
Russian drones attacked Cherkasy in central Ukraine, where emergency services reported that one person was injured and residential buildings and civil infrastructure suffered damage.
Ukrainian forces downed 69 of 165 drones launched overnight by Russia, the country’s Air Force said on Sunday.
Politics and diplomacy
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said he does not believe Russia will follow a three-day truce it declared to coincide with Moscow’s Victory Day celebrations on May 9. “This is not the first challenge, nor are these the first promises made by Russia to cease fire,” Zelenskyy said at a news conference with Czech President Petr Pavel.
Russian President Vladimir Putin said in a documentary released on Sunday that there had so far been no need to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine, and expressed “hope” that they would not be necessary.
United States President Donald Trump said he and his advisers have had “very good discussions” about Russia and Ukraine in recent days, without elaborating.
Moscow said that Chinese President Xi Jinping will visit Russia from May 7 to May 10, joining Putin at commemorations of the Allied victory against Nazi Germany.
Romania’s far-right presidential candidate, George Simion, who opposes military aid to Ukraine, decisively won the first round of the country’s rerun vote, setting up a contest with the centrist mayor of Bucharest, Nicusor Dan, on May 18.
Conflict Zones
Houthis maintain pressure on Israel as US launches more strikes on Yemen | Politics News

Prime minister of Yemen’s internationally recognised government has resigned amid political turmoil.
Israel has intercepted a missile fired from Yemen, the third such attack by Houthi forces in a 24-hour span, as the United States continues daily attacks on the country.
The Israeli army confirmed on Saturday it had activated air raid sirens across parts of the country following the missile launch.
No injuries or major damage were reported. Houthi spokesperson Yahya Saree claimed responsibility for the attack, calling it a response to Israeli operations in Gaza.
The Houthis have increasingly targeted Israel and shipping routes in the Red Sea, stating that their actions are acts of solidarity with Palestinians as Israel continues its assault on Gaza and the occupied West Bank.
The Houthis did not carry out attacks during the Gaza ceasefire earlier this year until Israel blocked all aid into the besieged enclave in early March and followed that with a full resumption of the war.
In the meantime, Houthi-affiliated Al Masirah TV reported on Saturday that the US launched two air raids on Yemen’s Kamaran Island and as-Salif district in the port city of Hodeidah.
The new attacks come a day after the same news outlet reported seven US attacks on the Ras Isa oil port in as-Salif district in Hodeidah. Last month, a US strike on the same port killed at least 80 people and wounded 150 in one of the deadliest attacks on the country by US forces.
The US has also ramped up its air campaign in Yemen, launching its most extensive military operations in the Middle East since President Donald Trump assumed office in January.
US forces claim to have struck Houthi positions, however, there have been numerous civilian casualties.
The high civilian toll from US strikes is drawing increasing alarm. The UK-based monitor Airwars reported that between 27 and 55 civilians were killed in March alone. April’s deaths are expected to be higher.
Houthi sources say at least 68 African migrants died in a single overnight strike on Monday, with additional casualties reported around the capital.
Yemen’s prime minister resigns
As the conflict intensifies, political instability is growing within Yemen.
Ahmed Awad bin Mubarak, the prime minister of the internationally recognised government, announced his resignation on Saturday, citing persistent challenges, including his inability to reshuffle the cabinet.
Government insiders said a power struggle with Presidential Council leader Rashad al-Alimi triggered Mubarak’s departure.
Within hours of the announcement, the presidential council named Finance Minister Salem Saleh bin Braik as prime minister, according to the state-run SABA news agency. The council also named bin Mubarak as an adviser to the ruling body, without addressing his claims.
Mubarak’s political career has been closely linked to the long-running war in Yemen. He rose to prominence after being abducted by Houthi fighters in 2015 while serving as chief of staff to then-president Abd-Rabbu Mansour Hadi.
Much of the international community does not recognise the Houthis, also known as Ansar Allah (supporters of God), even though the armed Iran-aligned group controls most parts of Yemen, including the capital, Sanaa, and some of the western and northern areas close to Saudi Arabia.
Conflict Zones
‘Don’t see a major war with India, but have to be ready’: Pakistan ex-NSA | Border Disputes News
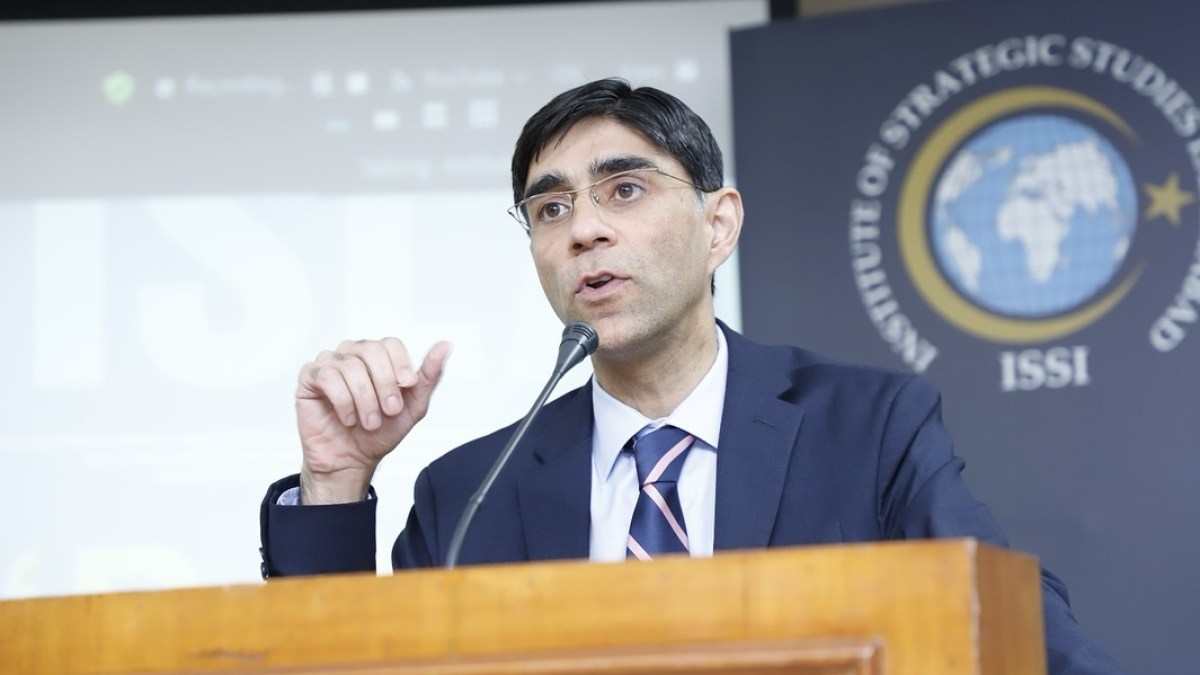

Islamabad, Pakistan – Eleven days after gunmen shot 26 people dead in the scenic valley of Baisaran in Indian-administered Kashmir’s Pahalgam, India and Pakistan stand on the brink of a military standoff.
The nuclear-armed neighbours have each announced a series of tit-for-tat steps against the other since the attack on April 22, which India has implicitly blamed Pakistan for, even as Islamabad has denied any role in the killings.
India has suspended its participation in the Indus Waters Treaty that enforces a water-sharing mechanism Pakistan depends on. Pakistan has threatened to walk away from the 1972 Simla Agreement that committed both nations to recognising a previous ceasefire line as a Line of Control (LoC) – a de-facto border – between them in Kashmir, a disputed region that they each partly control but that they both claim in its entirety. Both nations have also expelled each other’s citizens and scaled back their diplomatic missions.
Despite a ceasefire agreement being in place since 2021, the current escalation is the most serious since 2019, when India launched air strikes on Pakistani soil following an attack on Indian soldiers in Pulwama, in Indian-administered Kashmir, that killed 40 troops. In recent days, they have traded fire across the LoC.
And the region is now on edge, amid growing expectations that India might launch a military operation against Pakistan this time too.
Yet, both countries have also engaged their diplomatic partners. On Wednesday, United States Secretary of State Marco Rubio called Pakistani Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif and Indian Foreign Minister S Jaishankar, urging both sides to find a path to de-escalation. US Defence Secretary Pete Hegseth called his Indian counterpart, Rajnath Singh, on Thursday to condemn the attack and offered “strong support” to India.
Sharif met envoys from China, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, three of Pakistan’s closest allies, to seek their support, and urged the ambassadors of the two Gulf nations to “impress upon India to de-escalate and defuse tensions”.
To understand how Pakistani strategists who have worked on ties with India view what might happen next, Al Jazeera spoke with Moeed Yusuf, who served as Pakistan’s national security adviser (NSA) between May 2021 and April 2022 under former Prime Minister Imran Khan.
Prior to his role as NSA, Yusuf also worked as a special adviser to Khan on matters related to national security starting in December 2019, four months after the Indian government, under Prime Minister Narendra Modi, revoked the special status of Indian-administered Kashmir.

Based in Lahore, Yusuf is currently the vice chancellor of a private university and has authored and edited several books on South Asia and regional security. His most recent book, Brokering Peace in Nuclear Environments: US Crisis Management in South Asia, was published in 2018.
Al Jazeera: How do you assess moves made by both sides so far in the crisis?
Moeed Yusuf: India and Pakistan have for long struggled in terms of crisis management. They don’t have a bilateral crisis management mechanism, which is the fundamental concern.
The number one crisis management tool used by both sides has been the reliance on third parties, with the idea being that they would try and restrain them both and help de-escalate the crisis.
This time, I feel the problem India has run into is that they followed the old playbook, but the leader of the most important third party, the United States, didn’t show up to support India.
It appears that they have so far taken a neutral and a hands-off position, as indicated by President Donald Trump few days ago. (Trump said that he knew the leaders of both India and Pakistan, and believed that they could resolve the crisis on their own.)
Pakistan’s response is directly linked to the Indian response, and that is historically how it has been, with both countries going tit-for-tat with each other. This time too, a number of punitive steps have been announced.
The problem is that these are easy to set into motion but very difficult to reverse, even when things get better, and they may wish to do so.
Unfortunately, in every crisis between them, the retaliatory steps are becoming more and more substantive, as in this case, India has decided to hold Indus Water Treaty in abeyance, which is illegal as the treaty provides no such provision.
Al Jazeera: Do you believe a strike is imminent and if both sides are indicating preparedness for a showdown?
Yusuf: In such moments, it is impossible to say. Action from India remains plausible and possible, but the window where imminence was a real concern has passed.
What usually happens in crises is that countries pick up troop or logistics movements, or their allies inform them, or they rely on ground intelligence to determine what might happen. Sometimes, these can be misread and can lead the offensive side to see an opportunity to act where none exists or the defensive side to believe an attack may be coming when it isn’t the case.
Pakistan naturally has to show commitment to prepare for any eventuality. You don’t know what will come next, so you have to be ready.
Having said that, I don’t think we are going to see a major war, but in these circumstances, you can never predict, and one little misunderstanding or miscalculation can lead to something major.
Al Jazeera: How do you see the role of third parties such as the US, China and Gulf States in this crisis, and how would you compare it with previous instances?
Yusuf: My last book, Brokering Peace (2018) was on the third-party management in Pakistan-India context, and this is such a vital element for both as they have internalised and built it into their calculus that a third-party country will inevitably come in.
The idea is that a third-party mediator will step in, and the two nations will agree to stop because that is what they really want, instead of escalating further.
And the leader of the pack of third-party countries is the United States since the Kargil war of 1999. (Pakistani forces crossed the LoC to try to take control of strategic heights in Ladakh’s Kargil, but India eventually managed to take back the territory. Then-US President Bill Clinton is credited with helping end that conflict.)
Everybody else, including China, ultimately backs the US position, which prioritises immediate de-escalation above all else during the crisis.
This changed somewhat in the 2016 surgical strikes and 2019 Pulwama crisis when the US leaned heavily on India’s side, perhaps unwittingly even emboldening them to act in 2019.
(In 2016, Indian troops launched a cross-border “surgical strike” that New Delhi said targeted armed fighters planning to attack India, after gunmen killed 19 Indian soldiers in an attack on an army base in Uri, Indian-administered Kashmir. Three years later, Indian fighter jets bombed what New Delhi said were bases of “terrorists” in Balakot, in Pakistan’s Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, after the attack on the Indian military convoy in which 40 soldiers were killed. India and Pakistan then engaged in an aerial dogfight, and an Indian pilot was captured and subsequently returned.)
However, this time, you have a president in the White House who turned around and told both Pakistan and India to figure it out themselves.
This, I think, has hurt India more than Pakistan, because for Pakistan, they had discounted the possibility of significant US support in recent years, thinking they have gotten too close to India due to their strategic relationship.
But India would have been hoping for the Americans to put their foot down and pressure Pakistan, which did not exactly materialise. Secretary of State Marco Rubio’s phone call again is playing down the middle, where they are telling both the countries to get out of war.
So, what they have done has, oddly enough, still played a role in holding India back so far, since India didn’t (so far) feel as emboldened to take action as they may have during Pulwama in 2019.
Gulf countries have played a more active role than before. China, too, has made a statement of restraint.

Al Jazeera: How has Pakistan’s relationship with India evolved in recent years?
Yusuf: There has been a sea change in the relationship between the two countries. When I was in office, despite serious problems and India’s unilateral moves in Kashmir in 2019, we saw a ceasefire agreement on the Line of Control as well as back-channel talks.
We have tried to move ahead and reduce India’s incentive to destabilise Pakistan, but I think India has lost that opportunity due to its own intransigence, hubris and an ideological bent that continues to force them to demean and threaten Pakistan.
That has led to a change in Pakistan as well, where the leadership is now convinced that the policy of restraint did not deliver, and India has misused and abused Pakistan’s offers for dialogue.
The view now is that if India doesn’t want to talk, Pakistan shouldn’t be pleading either. If India does reach out, we will likely respond, but there isn’t any desperation in Pakistan at all.
This is not a good place to be for either country. I have long believed and argued that ultimately for Pakistan to get to where we want to go economically, and for India to get to where it says it wants to go regionally, it cannot happen unless both improve their relationship. For now, though, with the current Indian attitude, unfortunately, I see little hope.
Al Jazeera: Do you anticipate any direct India-Pakistan talks at any level during or after this crisis?
Yes – I don’t know when it will be, or who will it be through or with, but I think one of the key lessons Indians could probably walk away with once all this is over is that attempting to isolate Pakistan isn’t working.
Indus Water Treaty in abeyance? Simla Agreement’s potential suspension? These are major decisions, and the two countries will need to talk to sort these out, and I think at some point in future they will engage.
But I also don’t think that Pakistan will make a move towards rapprochement, as we have offered opportunities for dialogues so many times recently to no avail. As I said, the mood in Pakistan has also firmed up on this question.
Ultimately, the Indians need to basically decide if they want to talk or not. If they come forth, I think Pakistan will still respond positively to it.
*This interview has been edited for clarity and brevity.
Conflict Zones
Yemen’s Houthis launch missiles at Israel, army says it intercepts | Houthis News

The group says it attacked an Israeli military base with a hypersonic missile.
Yemen’s Houthis have claimed responsibility for launching two missiles towards northern Israel, targeting the Ramat David military airbase and the Tel Aviv area, as the group continues its military pressure in solidarity with Palestinians under Israeli fire.
The Israeli military said on Friday it intercepted the first missile and launched another interceptor at the second, which was also fired from Yemen.
Alarms were triggered in several locations, though authorities reported no casualties or damage. The military added that the outcome of the second interception was still under review.
Yahya Saree, spokesperson for the Houthis – also known as Ansar Allah – confirmed the group had carried a “military operation” against a key Israeli military target.
Saree said hypersonic missiles were used and had successfully hit their intended destination.
The Israeli army responded that “interception attempts were made” without providing further details.
The Houthi group has repeatedly said its attacks on Israel as well as United States and British ships in the Red Sea and Bab al-Mandeb Strait will only cease if Israel agrees to a permanent Gaza truce.
The Houthis did not carry out attacks during the Gaza ceasefire earlier this year until Israel blocked all aid into the besieged enclave in early March and followed that with a full resumption of the war.
Growing civilian death toll
The attacks come as the US escalates its military operations in Yemen.
Since March, the US has launched large-scale attacks not only on infrastructure but increasingly on individuals linked to the Houthi leadership.
Civilian casualties are mounting, with UK-based monitor Airwars estimating between 27 and 55 civilians were killed in March alone, and suggesting April’s toll is even higher.
One of the deadliest US strikes in April hit Ras Isa port in Hodeidah, killing at least 80 people and wounding more than 150.
On Monday at least 68 people were killed in the overnight strike on detained African migrants, and eight people were killed around the capital, Houthi media reported.
Rights advocates have been alarmed about the growing civilian death toll. Three US Democratic senators recently wrote to Pentagon chief Pete Hegseth, demanding an accounting for civilian lives lost.
“Strikes pose a growing risk to the civilian population in Yemen,” United Nations spokesperson Stephane Dujarric said on Monday. “We continue to call on all parties to uphold their obligations under international humanitarian law, including the protection of civilians.”
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoFear, pain, and a little hope: Volunteer doctors in Gaza | Israel-Palestine conflict News
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoIsraeli attacks kill two more as Syria government reaches deal with Druze | News
-

 Europe2 days ago
Europe2 days agoDetained Harvard researcher Kseniia Petrova says she didn’t lie to government
-

 Middle East2 days ago
Middle East2 days agoIran reasserts uranium enrichment rights as further US talks delayed | Nuclear Energy News
-

 Africa2 days ago
Africa2 days agoNguema takes power in Gabon
-
 Europe20 hours ago
Europe20 hours agoFather of crypto entrepreneur rescued from kidnappers after having finger severed
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoRoger Clemens: Red Sox great watches son Kody hit Fenway Park home run – for the Minnesota Twins
-

 Conflict Zones2 days ago
Conflict Zones2 days agoHouthis maintain pressure on Israel as US launches more strikes on Yemen | Politics News




