Seoul, South Korea
CNN
—
Europe is staring down the barrel of a stark new reality where the United States being the backbone of NATO – the alliance that has guaranteed the continent’s security for almost 80 years – is no longer a given.
President Donald Trump’s public animosity towards Ukraine’s Volodymyr Zelensky, his willingness to embrace Russia’s Vladimir Putin and recent comments casting doubt over whether he would defend NATO allies “if they don’t pay” have all forced European leaders to start thinking the previously unthinkable – is the US a reliable security partner at a time when the continent is being rocked by its biggest war since the 1940s?
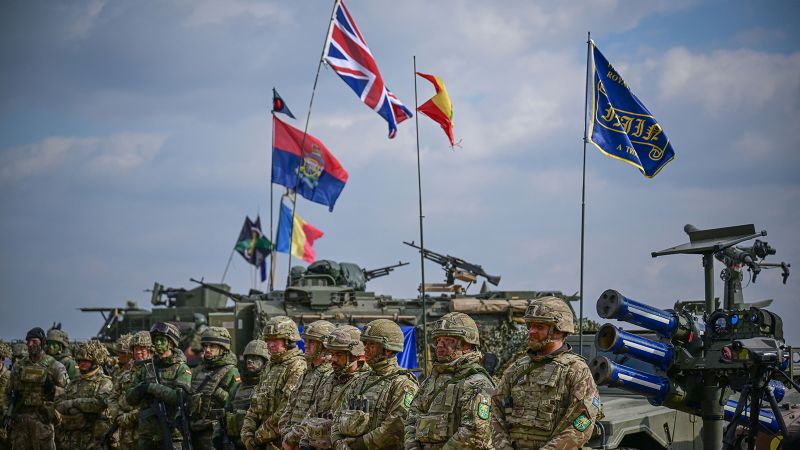
But NATO without the US is far from impotent, with more than a million troops and modern weaponry at its disposal from the 31 other countries in the alliance. It also has the wealth and technological knowhow to defend itself without the US, analysts say.
The US and Germany are the biggest contributors to NATO’s military budget, civil budget and security investment program, at almost 16% each, followed by the UK at 11% and France at 10%, a NATO fact sheet says. Analysts say it wouldn’t take much for Europe to make up for the loss of Washington’s contribution.
If European countries unite and buy the right equipment, Europe “could pose a serious conventional and … nuclear deterrent” to Russia, Ben Schreer, Europe executive director of the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS), said in a Zoom call with CNN and other journalists in late February.

“Europe alone (still has) a capacity to muster the resources it would need to defend itself, it’s just a question of whether (it is) willing to,” Schreer said.
And that’s the key question. Over more than 75 years and the administrations of 14 different US presidents, including the first Trump administration, the US has been the sinew that has kept the alliance together.
During the Cold War, US troops on the continent were there as a deterrent to any Soviet ambitions to expand the Warsaw Pact alliance and eventually saw out its end when the Berlin Wall fell in 1989. NATO campaigns in the Balkans in the 1990s were conducted with US troops and airpower. And, until the second Trump administration took office on January 20, Washington spearheaded aid for Ukraine.
Those decades of trans-Atlantic solidarity may have come to an end in recent days, analysts say.
Trump’s Oval Office blow-up with Zelensky – after which he halted US aid to Kyiv – “felt like a deeper rupture, not just with Ukraine, but with the US ‘free world’ strategy from Truman through Reagan,” Dan Fried, a senior fellow at the Atlantic Council and former US assistant secretary of state for Europe, said on the council’s website.
John Lough, a former NATO official who is now an associate fellow at the Chatham House think tank in London, sees an even more profound split in the alliance.
“It simply feels that the United States sees Europe more as a competitor, a rival, than an ally,” Lough told CNN, adding that because of that the commitment for Washington to defend NATO allies is somewhat in doubt.
It’s a fracture that Lough sees as unrepairable.
“Once you start to lose part of that commitment, you effectively lose it all,” Lough said.
Some people in European circles are starting to ask whether Washington should be described “in some ways as an enemy,” he said.
But some analysts say a NATO without the US is not a bad idea.
“As soon as US allies become convinced that they can no longer trust in US capabilities to defend them when push comes to shove, they will rush to pick up the slack and work towards growing their own capabilities,” Moritz Graefrath, a postdoctoral fellow in security and foreign policy at William & Mary’s Global Research Institute, wrote in War on the Rocks last year.
“It is in this sense that — perhaps counterintuitively — a withdrawal of US forces will create an even stronger, not weaker, Europe,” Graefrath wrote.
Prime Minister of NATO member Poland, Donald Tusk, thinks this process has started already.
“Europe as a whole is truly capable of winning any military, financial, economic confrontation with Russia – we are simply stronger,” he said ahead of a European Union summit this week. “We just had to start believing in it. And today it seems to be happening.”
In concept, a European military could be formidable.
Turkey has NATO’s largest armed forces after the United States, with 355,200 active military personnel, according to the Military Balance 2025, compiled by the IISS. It’s followed by France (202,200), Germany (179,850), Poland (164,100), Italy (161,850), the United Kingdom (141,100), Greece (132,000) and Spain (122,200).

Turkey also has the most army personnel, which make up of the majority of frontline ground troops, with 260,200, France (113,800), Italy (94,000), Greece (93,000), Poland (90,600) the UK (78,800), Spain (70,200) and Germany (60,650), according to the IISS report.
In contrast, there were about 80,000 US troops assigned or deployed to bases in NATO countries as of June 2024, a July 2024 report from the Congressional Research Service (CRS) says.
Most of those US troops are in Germany (35,000), Italy (12,000) and the UK (10,000), the CRS says.
Some of the larger NATO nations also have weapons equal to or many times better than what Russia has.
Take aircraft carriers for instance. While Russia has a single, antiquated aircraft carrier, the UK alone has two modern carriers capable of launching F-35B stealth fighters. France, Italy and Spain field aircraft carriers or amphibious ships capable of launching fighter jets, according to the Military Balance.
Aside from the US, France and the UK maintain nuclear forces, with both deploying ballistic missile submarines.
The NATO allies besides the US have about 2,000 fighter and ground-attack jets among them, with dozens of new F-35 stealth jets included in that number.
Ground forces include modern tanks, including German Leopards and British Challengers, donated units of which are now serving in the Ukrainian military. European NATO countries can field powerful cruise missiles, like the joint Franco-British SCALP/Storm Shadow, which has also proven itself on the Ukrainian battlefield.
The Military Balance 2025 report notes that Europe is taking steps to improve its military forces without US help. In 2024, six European countries united in a project to develop ground-launched cruise missiles, made moves to increase munitions production capacity and to diversify their supplier base, looking to countries like Brazil, Israel and South Korea as new sources for military hardware.
Analysts say even if the US were to completely pull out of Europe, it would leave important infrastructure behind.
The US has 31 permanent bases in Europe, according to the Congressional Research Service – naval, air, ground and command-and-control facilities that would be available to the countries where they are located if the US were to leave.
And Graefrath notes, that infrastructure would not be lost to Washington if there is regret after a possible US withdrawal.
“It leaves much of the US military infrastructure intact for an extended period (ensuring) that the United States retains the ability to make a military return if Europe were to fail to respond as predicted,” he wrote.
Some hope that the talk of a US withdrawal from NATO is just Trump bluster aimed at pushing allies to cough up and spend more on defense.
They say the world, and another key US alliance, have been here before – during Trump’s first administration, when he reportedly asked the Pentagon to look at options for drawing down US troops stationed in South Korea as protection against nuclear-armed North Korea.
That came as Trump prepared for meetings with North Korean dictator Kim Jong Un at which he hoped to persuade Kim to commit to giving up his nuclear arsenal.

A source close to the White House told CNN at the time that a US troop pullout was viewed as something that could possibly happen in the future but “not until long after (North Korea’s) nukes are verifiably gone.”
But Kim rejected all entreaties for him to give up his nuclear weapons program.
The Trump-Kim meeting “was sold as a big success despite that fact that it wasn’t,” said Schreer.
Afterward, the US returned to “business as usual” on the Korean Peninsula, Schreer said. The US – with tens of thousands of troops in South Korea – kept them there. Bilateral exercises with Seoul’s forces resumed, US warships visited South Korean ports and US Air Force bombers flew over the region.
The same could occur in Europe if Trump doesn’t get what he wants from Putin, analysts said. NATO could go on, with the recent threats to depart just a small bump in the road.
“If Putin tries to … screw Donald too much, even Donald Trump might recognize that,” Schreer said.